Fire Hazard Classification
Fire hazard classification When designing a fire sprinkler system, the hazard class (LH, OH, HH) determine the characteristics of the fire sprinkler installation for the specification of water supply, number of fire pumps, number of sprinklers, and so on.

Fire hazard classification. My feeling is that the fire loading is very low, and it could be considered Light Hazard Your thoughts?. Classification of fire CLASS A FIRES Class A fires (designation symbol is a green triangle) involve ordinary combustible materials like paper, wood and fabrics, rubber CLASS B FIRES CLASS C FIRES CLASS D FIRES CLASS K FIRES. And hazard classification of the material Up to the MAQ for each class of hazardous material is permitted in each control area (IBC) The concept of the control area is to limit the maximum allowable quantity (MAQ) of hazardous materials per control area rather than per building, and then limit the number of control areas within each.
Hazard classifications National Fire Protection Association (NFPA) hazard classifications for flammable and combustible liquids are listed below Hazard classification for flammable liquids Class. The hazard class of dangerous goods/commodities is indicated either by its class (or division) number or name Placards are used to identify the class or division of a material Division 13 Explosives which have a fire hazard and either a minor blast hazard or a minor projection hazard or both, but not a mass explosion hazard. Class C Class C fires are fires involving energized electical equipment such as computers, servers, motors, transformers, and appliances Remove the power and the Class C fire becomes one of the other classes of fire Class D Class D fires are fires in combustible metals such as magnesium, titanium, zirconium, sodium, lithium, and potassium.
Fireretardant chemicals are required by the Consumer Product Safety Commission (CPSC) to be added to these materials to reduce the flammability hazard Unfortunately, the chemical additives tend to break down with time and lose their effectiveness. Fire Hazard 1 FIRE HAZARDS 2 What is a fire hazard?. Another category of fire hazards are situations and events that impede fire protection and prevention methods This can include impediments to firefighting, compromised builtin fire safety systems, and situations that restrict the escape of people from an affected building or area in the event of a fire.
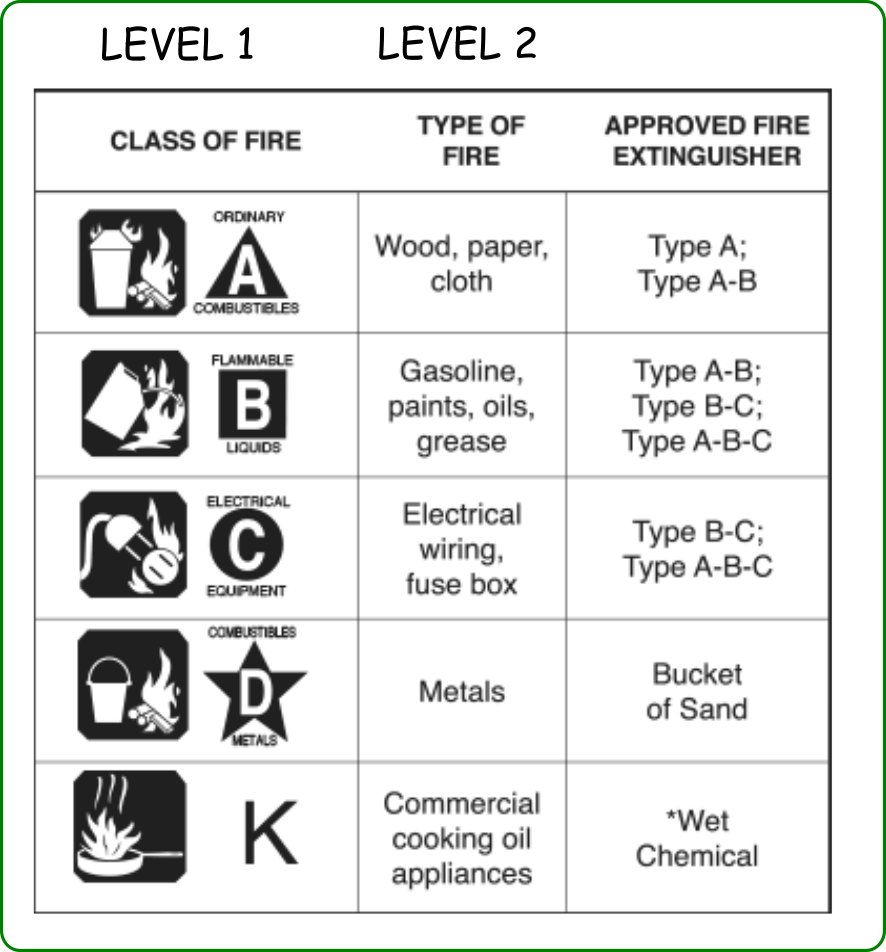
Class K – cooking greases and fats Class A, B and C extinguishers are often found in homes and businesses;. 5 Types of Occupancy Classifications for Fire Sprinklers in Maryland Light Fire Hazard The first classification to be aware of is known as the light hazard In these spaces, there are not Ordinary Fire Hazard – Group 1 Under this category, the fire sprinklers are still necessary, but there is a. Fire hazard classification When designing a fire sprinkler system, the hazard class (LH, OH, HH) determine the characteristics of the fire sprinkler installation for the specification of water supply, number of fire pumps, number of sprinklers, and so on The hazard class to which the sprinkler system is to be designed shall be determined before starting the design work.
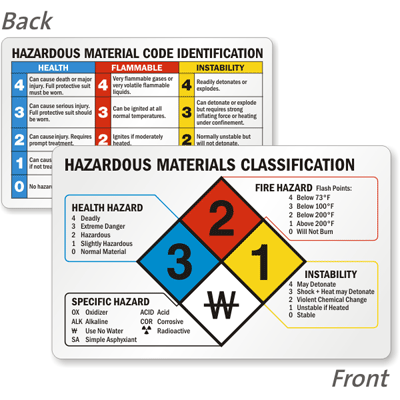
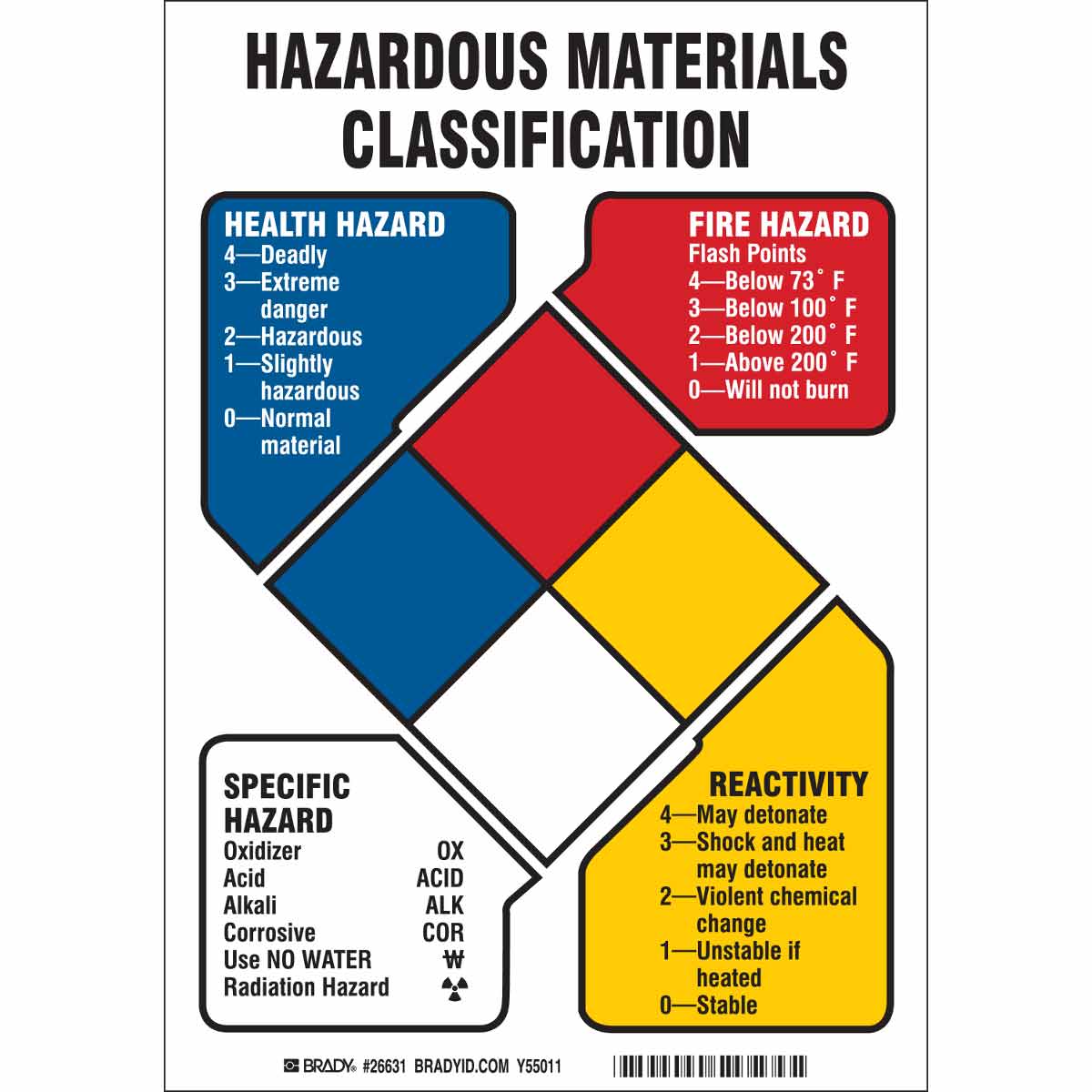
A1 Classification The cladding materials that fall under the A1 fire classification are ones with the highest performance These materials are noncombustible in nature and have no contribution to fire at all Classification The construction cladding materials of cladding have limited combustibility properties. This is a digital Seismic Hazard Zone Map presenting areas where landslides may occur during a strong earthquake Three types of geological hazards, referred to as seismic hazard zones, may be featured on the map 2) earthquakeinduced landslides State Special Study Fault Zones (Aluist Priolo) (state_special_study_zoneszip) 169 KB Download. The blue, red, and yellow fields—which represent health hazard, flammability, and reactivity, respectively—use a numbering scale ranging from 0 to 4 A value of 0 means that the material poses essentially no hazard, whereas a rating of 4 indicates extreme danger The white field is used to convey special hazards.
ICC Digital Codes is the largest provider of model codes, custom codes and standards used worldwide to construct safe, sustainable, affordable and resilient structures. Another category of fire hazards are situations and events that impede fire protection and prevention methods This can include impediments to firefighting, compromised builtin fire safety systems, and situations that restrict the escape of people from an affected building or area in the event of a fire. 35 Classification of Hazard It is selection of extinguishing agents for the specific class(es) of occupancy hazards to be protected and is classified as follows a) Light (Low) hazard b) Ordinary (Moderate) hazard c) Extra (High) hazard 36 Classification of Occupancy Hazard.
In 07, CAL FIRE classified areas within its state firefighting responsibility area (SRA) as belonging to one of several fire hazard severity classifications moderate fire severity hazard (yellow on map), high fire severity hazard (orange), very high fire severity hazard (red), and unzoned (gray) Maps of these fire hazard zones have been published on CAL FIRE's website, along with the corresponding GIS data used to generate the maps. Common Name Chemical Name(s) Chemical Concentrations CAS Number(s) NFPA Code (HFR) Hazard Code Acetone Acetone (2propanone) 100% 130 FLA Acetylene Acetylene, compressed gas 100% 143 FLG, OHH Adhesive Remover Mineral Spirits. The Hazardous Materials Identification System (HMIS) is a numerical hazard rating that incorporates the use of labels with color developed by the American Coatings Association as a compliance aid for the OSHA Hazard Communication (HazCom) Standard.
Classification of Occupancy & Hazard of Contents As Defined by NFPA 101® Life Safety Code® & NFPA 5000™ Building Construction & Safety Code (09) Classification of Occupancy (61) The occupancy of a building or structure, or portion of a building or structure, shall be classified as one of the following to Assembly. Each of health, flammability and reactivity is rated on a scale from 0 (no hazard) to 4 (severe hazard) The latest version of NFPA 704 sections 5, 6, 7 and 8 for the specifications of each classification are listed below. The hazard class of dangerous goods/commodities is indicated either by its class (or division) number or name Placards are used to identify the class or division of a material Division 13 Explosives which have a fire hazard and either a minor blast hazard or a minor projection hazard or both, but not a mass explosion hazard.
The classification is broken into four categories health, fire, specific hazard, and reactivity This universal system of classification alerts others of the potential dangers ahead and how to treat them What Do the Colors Mean?. The classification is broken into four categories health, fire, specific hazard, and reactivity This universal system of classification alerts others of the potential dangers ahead and how to treat them What Do the Colors Mean?. For more fire safety tips, be sure to follow us on Facebook, Twitter, and LinkedIn Categories Fire Solutions s commodity classifications , fire solutions , and fire sprinklers This entry was posted on Friday, July 5th, 19 at 1243 pm.
Hazard Class General Description;. Pancy it most nearly resembles based on the fire safety and relative hazard Occupied roofs shall be classified in the group that the occupancy most nearly resembles, according to the fire safety and relative hazar d, and shall comply with Section 1 Assembly (see Section 303) Groups A1, , A3, and A5 2. Test methods or guidelines for hazard classification of energetic materials used for inprocess operations shall be approved by the fire code official Test methods used shall be that have a fire hazard and either a minor blast hazard or a minor projection hazard or both, but not a mass explosion hazard The major hazard is radiant heat or.
By understanding what each fire class means, you can understand which fire types are a safety hazard at your business Once you are aware of what types of fires your business may encounter, you can buy the proper extinguisher for protecting against them Class A Class A fires are defined as ordinary combustibles. Each of health, flammability and reactivity is rated on a scale from 0 (no hazard) to 4 (severe hazard) The latest version of NFPA 704 sections 5, 6, 7 and 8 for the specifications of each classification are listed below. Class B – The Fires which involve the liquids or the liquefied solids such as the paints, Fats or Oils These can be further subdivided or partitioned into Class B1 – The fires that involve the liquids which are solvable in the water such as the methanol They can be extinguished by the carbon dioxide, water spray, dry powder, light water, and the vaporizing liquids.
And Class K, in commercial kitchens In addition to the fire hazard classification, a numerical rating measures the extinguishing potential of type A and B extinguishers. Hazard classification is the process of evaluating the full range of available scientific evidence to determine if a chemical is hazardous, as well as to identify the level of severity of the hazardous effect When complete, the evaluation identifies the hazard class(es) and associated hazard. While occupancy classifications help to design for the severity of the fire hazard that sprinklers must protect for, commodity classifications provide additional, more specific information regarding the factors that contribute to that fire hazard Commodity classifications in NFPA 13 are based on the type and quantity of materials present in a.
The aim of this study was to examine fire safety measures and their viability in buildings, the required measures are technology based The relevant hazard classification of the system f or. The type of hazard and extinguisher rating C Required in areas where energized electrical equipment may be encountered Fires involve energized electrical equipment A Class C rating is only put on extinguishers that already have a Class A or Class B rating A Class A, Class B, or Class A & B extinguisher gets. Each of health, flammability and reactivity is rated on a scale from 0 (no hazard) to 4 (severe hazard) The latest version of NFPA 704 sections 5, 6, 7 and 8 for the specifications of each classification are listed below.
Write in the Phoenix Fire Code Hazard Classification for each chemical (ex oxidizer, corrosive, flammable liquid, etc) To determine the hazard classification, refer to the product MSDS You may also need to refer to the Phoenix Fire Code to accurately make this determination. Determine the Occupancy Hazard Classification Number The occupancy hazard rating is a way to classify an occupancy with a number that can be used in the formula to determine minimum water suppliesneeded for the structure In the formula, the occupancy hazard number ranges from 3 through 7, and the occupancies with a greater hazard receive. Each of health, flammability and reactivity is rated on a scale from 0 (no hazard) to 4 (severe hazard) The latest version of NFPA 704 sections 5, 6, 7 and 8 for the specifications of each classification are listed below.
Class B – The Fires which involve the liquids or the liquefied solids such as the paints, Fats or Oils These can be further subdivided or partitioned into Class B1 – The fires that involve the liquids which are solvable in the water such as the methanol They can be extinguished by the carbon dioxide, water spray, dry powder, light water, and the vaporizing liquids. Hazard class/division Hazard description 11 Mass explosion 12 Nonmass explosion, fragmentproducing 13 Mass fire, minor blast or fragment 14 Moderate. Each section in the NFPA Hazard Classification is represented by a different color and classification.
Common Name Chemical Name(s) Chemical Concentrations CAS Number(s) NFPA Code (HFR) Hazard Code Acetone Acetone (2propanone) 100% 130 FLA Acetylene Acetylene, compressed gas 100% 143 FLG, OHH Adhesive Remover Mineral Spirits. • Conditions that favor fire development or growth • Oxygen, fuel, and heat • Fire hazards usually involve the mishandling of fuel or heat • Fire or combustion is a chemical reaction between oxygen and a combustible fuel • Source of ignition= Spark, flame and high temperature are needed. Electrical fires are fires involving potentially energized electrical equipment The US system designates these "Class C";.
Hazardous because flammable gases or vapors are present (or may be present) in quantities sufficient to produce explosive or ignitable mixtures Class II Hazardous because combustible or conductive dusts are present (or may be present) in quantities sufficient to produce explosive or ignitable mixtures Class III. Fire Sprinkler Hazard Classifications Defined Light Hazard These are locations where combustible products and the quantity of Class A combustibles and Class B Low Hazard These are locations where combustibility and the quantity of Class A combustibles and Class B flammables Ordinary Hazard. By understanding what each fire class means, you can understand which fire types are a safety hazard at your business Once you are aware of what types of fires your business may encounter, you can buy the proper extinguisher for protecting against them Class A Class A fires are defined as ordinary combustibles.
Cdafd (Specifier/Regulator) 26 Jun 14 1559 Sounds good Unless they are storing kegs of acetone Get a chemical list RE Beauty Salon Occupancy Hazard?. Hazardous materials are chemicals that pose a physical hazard (like fire or explosion) or a health hazard (like toxic or corrosive) This guide treats hazardous waste as a hazardous material This Chemical Classification Packet meets the requirements of the HMIS (Hazardous Materials Inventory Statement) in the CFC. Increased risk of explosion if desensitizing agent is reduced Desensitized explosives Category 1 Danger P210, P212, P230, P233, P280 P370P380P375 P401 P501 H7 Fire or projection hazard;.
The Australian system designates them "Class E" This sort of fire may be caused by shortcircuiting machinery or overloaded electrical cables. Flammable gases Flammable aerosols Flammable liquids Flammable solids These four classes cover products that have the ability to ignite (catch fire) easily and the main hazards are fire or explosion. SCEngr1 (Structural) (OP) 22 Aug 07 1557 For a 10'x12' automotive paint mixing room (closed cap system), can we provide the onehour fire barrier between this room and the retail space WITHOUT installing an automatic sprinkler system?.
SPRINKLER PROTECTION BASICS HAZARD CLASSIFICATION ORDINARY HAZARD, GROUP 2 C Quantity of combustibles is moderate to high and C Combustibility of contents is moderate to high and C Storage heights do not exceed 12 feet and C Moderate to high rates of heat release expected C Examples. The fuel for the fire, as follows Class A—fires involving ordinary combustibles, such as paper, trash, some plastics, wood and cloth A rule of thumb is if it leaves an ash behind, it is a Class A fire Class B—fires involving flammable gases or liquids, such as propane, oil and gasoline Class C—fires involving energized electrical. Each of health, flammability and reactivity is rated on a scale from 0 (no hazard) to 4 (severe hazard) The latest version of NFPA 704 sections 5, 6, 7 and 8 for the specifications of each classification are listed below.
Hazard classification for flammable liquids Class Flash point Boiling point Examples IA below 73°F (23°C) below 100°F (38°C) diethyl ether, pentane, ligroin, petroleum ether IB below 73°F (23°C) at or above 100°F (38°C) acetone, benzene, cyclohexane, ethanol IC °F (2438°C)pxylene Hazard classification for. Increased risk of explosion if desensitizing agent is reduced Desensitized explosives Category 2 Danger P210, P212, P230, P233, P280. For gases, vapours and mists the zone classifications are recognised as Zone 0, Zone 1 and Zone 2 areas Let’s take a look at what defines each zone Zone 0 Zone 0 is an area in which an explosive atmosphere is present continuously for long periods of time or will frequently occur Zone 1.
Fire, blast or projection hazard;. Class 1 (Explosives) Six divisions – –11 –Mass explosion hazard –affects entire load instantaneously –12 –Projection hazard –not mass explosion hazard –13 –Fire hazard & minor blast/projection hazard 10b. FIRE HAZARD CLASSIFICATIONS In its NFPA 10, Standard for Portable Fire Extinguishers, the National Fire Protection Association (NFPA) identifies five primary classifications of fire hazards Identifying these can help you select the appropriate extinguisher Class A – ordinary combustible materials, such as wood, cloth, paper, rubber and plastic.
Interpreting Test Results to Obtain Classification Material classification of fire performance is based on the test results in accordance with the Life Safety Code, NFPA 101 Section 1023 and the Standard Building Code (issued by SBCCI) Section 704 and/or Uniform Building Code (UBC). Category 1 is always the greatest level of hazard (that is, it is the most hazardous within that class) If Category 1 is further divided, Category 1A within the same hazard class is a greater hazard than category 1B Category 2 within the same hazard class is more hazardous than category 3, and so on There are a few exceptions to this rule. Class D, in factories;.
Class B fires are fires in flammable liquids such as gasoline, petroleum greases, tars, oils, oilbased paints, solvents, alcohols Class B fires also include flammable gases such as propane and butane Class B fires do not include fires involving cooking oils and grease. 6224* High Hazard Contents High hazard contents shall be classified as those that are likely to burn with extreme rapidity or from which explosions are likely This classification would not necessarily apply to a small janitor’s closet or a small collection of incidentaluse chemicals. Each section in the NFPA Hazard Classification is represented by a different color and classification The.
SCEngr1 (Structural) (OP) 22 Aug 07 1557 For a 10'x12' automotive paint mixing room (closed cap system), can we provide the onehour fire barrier between this room and the retail space WITHOUT installing an automatic sprinkler system?. RE Beauty Salon Occupancy Hazard?. ICC Digital Codes is the largest provider of model codes, custom codes and standards used worldwide to construct safe, sustainable, affordable and resilient structures.
The hazard class of dangerous goods/commodities is indicated either by its class (or division) number or name Placards are used to identify the class or division of a material Division 13 Explosives which have a fire hazard and either a minor blast hazard or a minor projection hazard or both, but not a mass explosion hazard.

Fire Hazard Rating Map Of The Study Area Download Scientific Diagram

Hazardous Materials Classification Health Hazard Fire Hazard Specific Hazard Instability Build Your Own Sign From A Kit Light Weight Plastic Sign With Holes 14 X 10 Industrial Warning Signs Amazon Com Industrial

Fire Safety Resources Fire Safety Online Courses Esky Learning Online
Fire Hazard Classification のギャラリー

Nfpa Hazard Classification System

Hazardous Materials Classification Sign Small

09 Sfpe San Diego A Fundamental Approach Towards Fire Hazard Cl
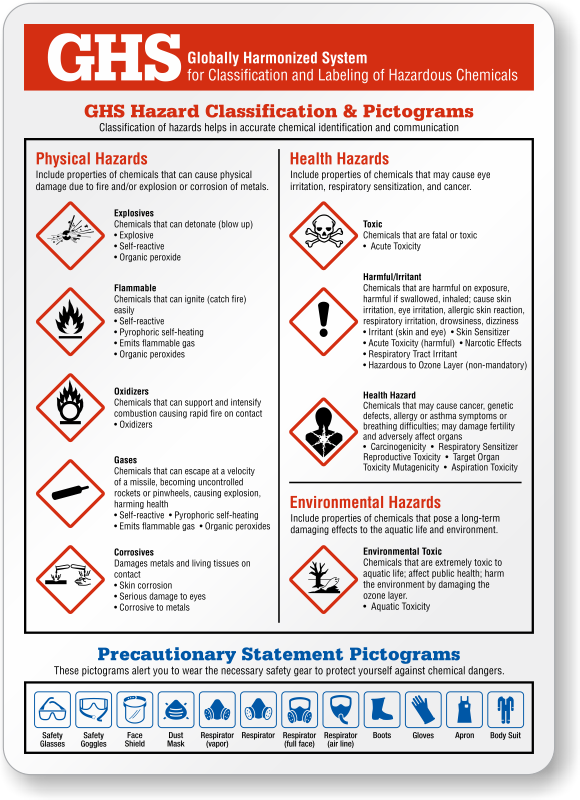
Ghs Classification Labeling Of Hazardous Chemicals Poster Sku S2 1473
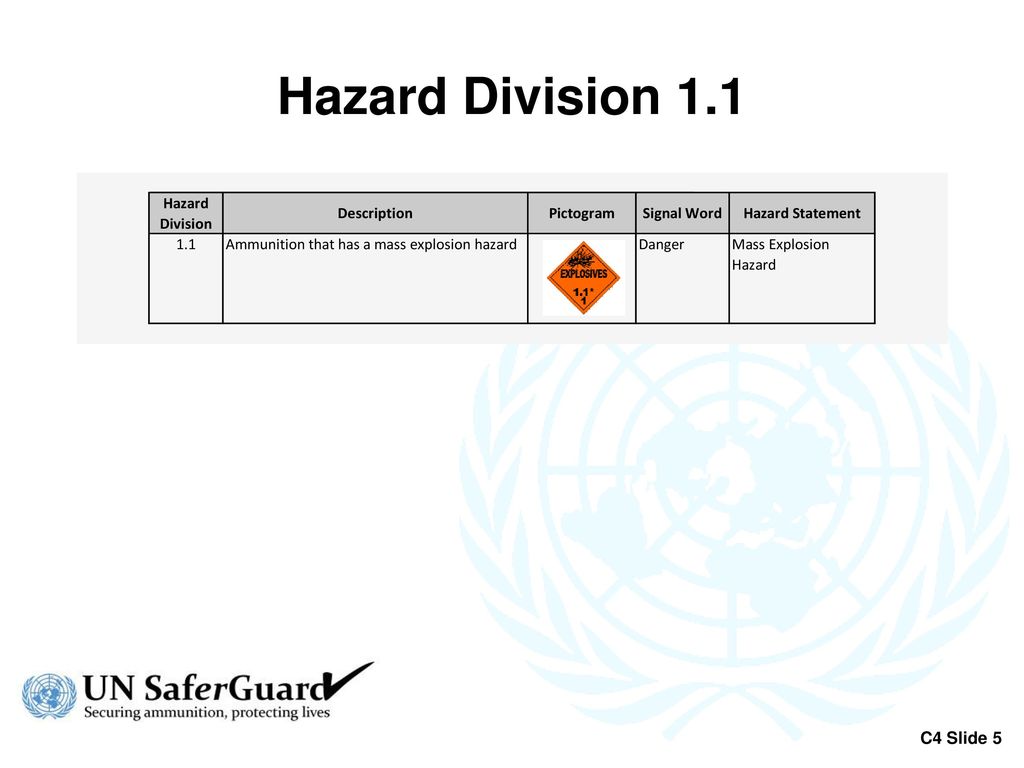
Un Hazard Classification Codes Hcc Ppt Download

Classifications Www Petropanels Com
1

Classification Labelling Transport Of Hazardous Goods

Fire Hazard Classification Uk National Lottery
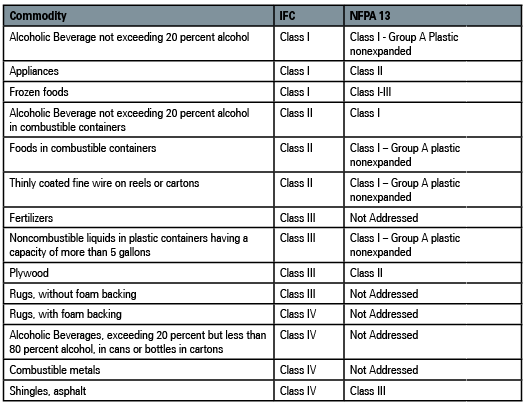
Commodity Classifications Sprinkler Age

Fire Hazard Rating Index For Modelling Download Table

Amazon Com Hazardous Materials Classification Health Hazard Fire Hazard Specific Hazard Instability Engineer Grade Reflective Labels 14 X 10 Office Products

09 Sfpe San Diego A Fundamental Approach Towards Fire Hazard Cl

Lecture 9 Fire Hazard

Nfpa Diamond Classification Chart Seton

Classification Of Fire Hazard For Forest Districts In Accordance With Download Scientific Diagram
2
2

Dow S Fire And Explosion Index Hazard Clasification Guide By Anahi Salas Issuu

Hazardous Materials Classification Sign 11x8 Sticker Health And Safety Poster Hazardous Materials Chemical Safety
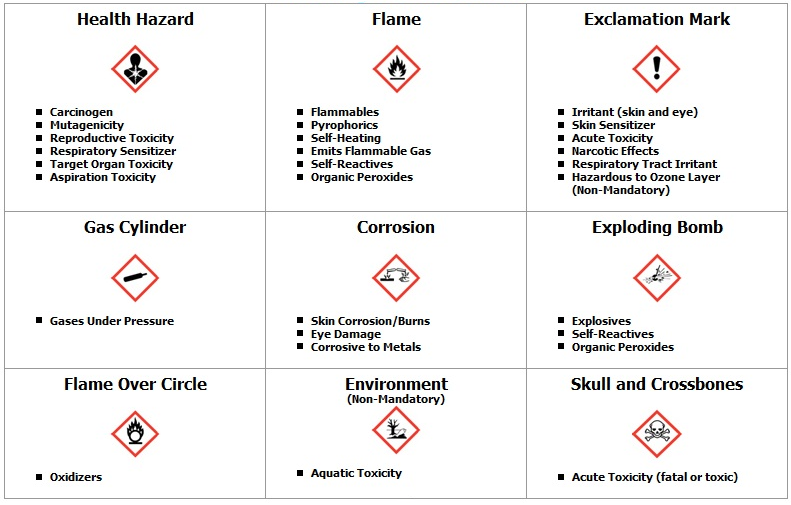
Division Of Research Safety Illinois

Hazardous Materials Classification Sign 11x8 Rigid Plastic Health And Safety Poster Hazardous Materials Chemical Safety
Onlinelibrary Wiley Com Doi Pdf 10 1002 Prs
Hazardous Materials Classification Wallet Card Signs
2
2

Abcs Of Fire Extinguishers Fire Prevention Services The University Of Texas At Austin
What Constitutes A Good Risk Taxonomy Open Risk

Hazardous Materials Classification Sign Kit

Fhc Fire Hazard Classification By Acronymsandslang Com
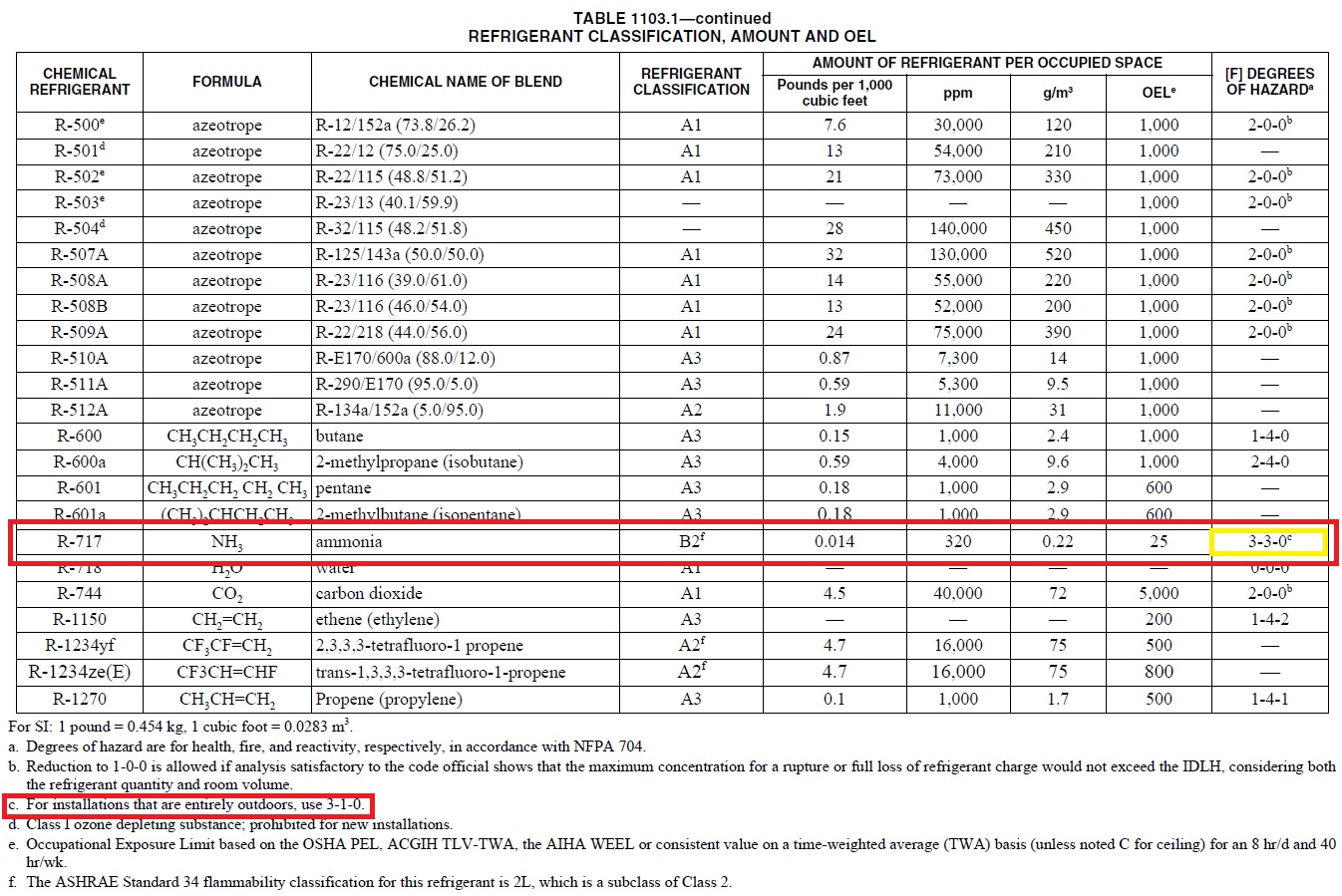
Q A Nfpa 704 And Ammonia

Basic Guide To Nfpa 13 Occupancy And Commodity Classifications

1 Wildland Fire Hazard Severity Classification Analysis By Fuel Type Download Table

Classification Of Fire Hazard Grade For Material In Different Download Scientific Diagram

Sprinkler Design Fse 221 Fire Protection Systems Ppt Video Online Download

Fire Regulations For Buildings
Brady Part Nfr Health Hazard Fire Hazard Specific Hazard Reactivity Sign Bradyid Com

How Many Fire Extinguishers Are Required And Where Nfpa
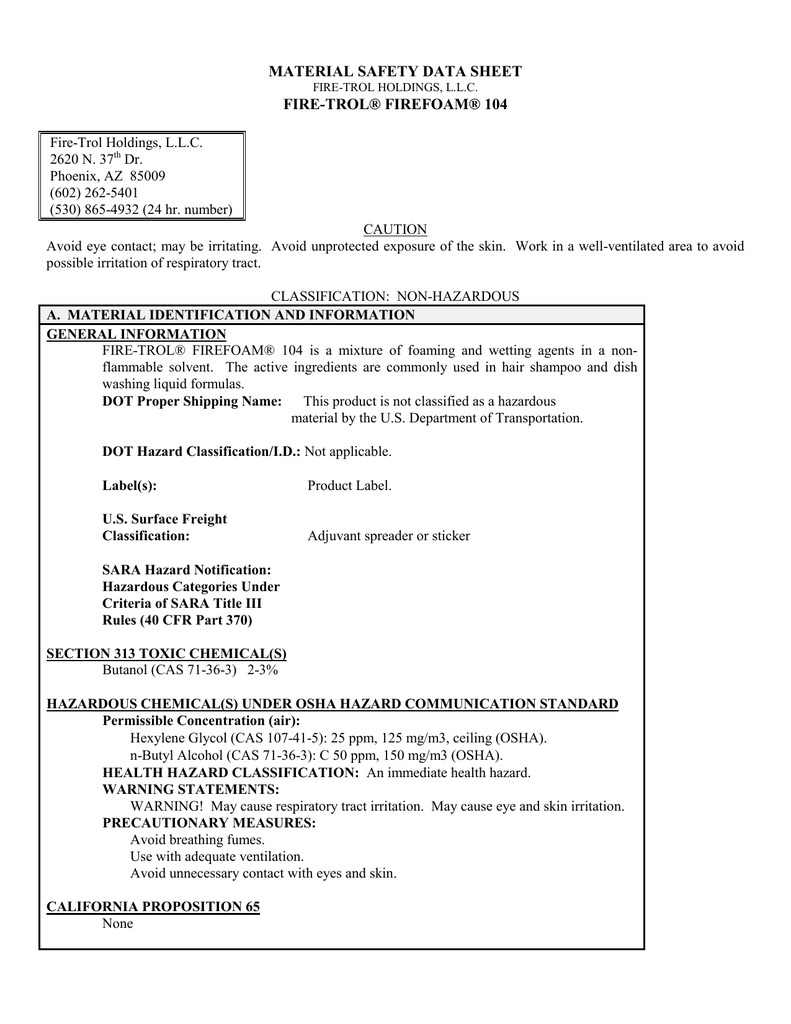
Material Safety Data Sheet Fire Trol Firefoam 104

Chapter 3 Simulating Fire Hazard Across Landscapes Through Time Integrating State And Transition Models With The Fuel Characteristic Classification System Pacific Northwest Research Station Pnw Us Forest Service

Cook Lab Plants Microbes Genes Hazardous Chemicals Description And Symbols

Classification Of The Spatial Patterns Of Fire Hazard By Zone Download Scientific Diagram

Sprinklers Australian Building Services

Fire Sprinkler Hazard Classifications Defined Compliance First Inc

Nfpa Hazardous Materials Classification Safety Signs W Graphic

Dow S Fire Explosion Index Hazard Classification Guide 7th Edition Aiche
Read Free Full Ebook Download Dows Fire And Explosion Index Hazard Classification Guide Full Ebook Online Free Video Dailymotion

Dow S Fire And Explosion Index Hazard Clasification Guide By Anahi Salas Issuu

Hazardous Materials Classification Nfpa 704 Basics

Chapter 2 Rationale For Classification Of Combustible Dusts Classification Of Dusts Relative To Electrical Equipment In Class Ii Hazardous Locations The National Academies Press

Hazard Classification System Ppt Download

Appendix A Material Factors And Properties Dow S Fire Explosion Index Hazard Classification Guide Wiley Online Library

Review Of The Fire Risk Hazard And Thermomechanical Response Of Bridges In Fire

Abl Rocking Buffer Msds Illumina
Www Sjgov Org Uploadedfiles Sjc Departments Ehd Forms Ehd guidance for correcting obsolete federal hazard categories Pdf
2
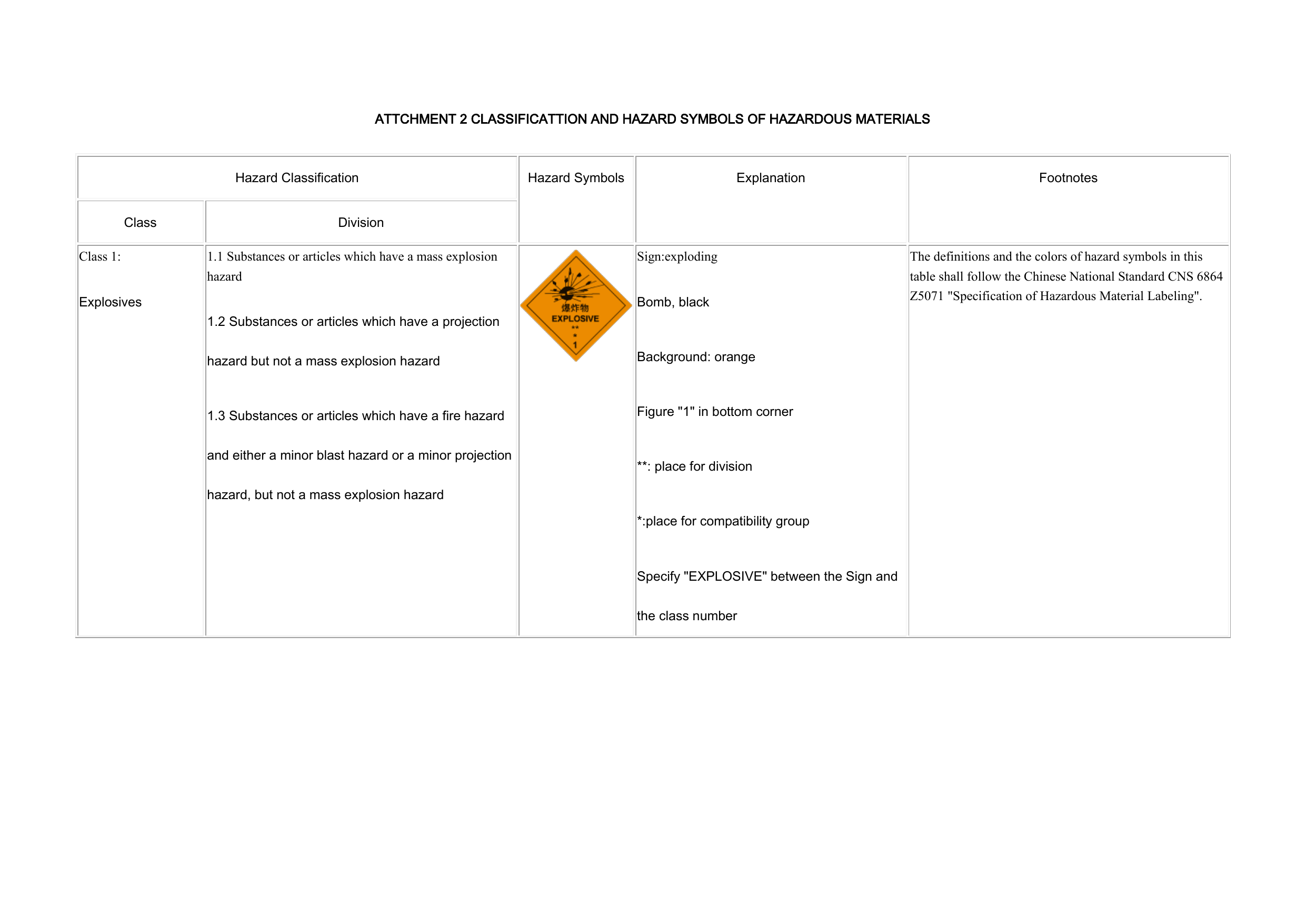
Attchment 2 Classificattion And Hazard Symbols Of Hazardous Materials

Hazard Classification Of Post Fire Debris Flows Download Table
Www Ispeboston Org Download 19 06 12 Stills Safina Pdf

Ppt Hazard Communication Powerpoint Presentation Free Download Id

The Fire Triangle Hazardous Materials Classification Coolguides

Brady Self Sticking Polyester 7 X 10 Sign Legend Hazardous Materials Classification Health Hazard 4 Deadly Industrial Warning Signs Amazon Com Industrial Scientific

Hazardous Materials Classification Sign 14x10 040 Alum Hazard Identification Chemical Safety Identification System

Fm 4 30 13 Chptr8 Fire Protection Prevention And Safety Awareness

Engineering Standard For Classification Of Fires And Fire Hazard Manualzz

Nfpa Classification Diamond Roll Labels Emedco

Ppt Cen Hazard Classification For Sprinklers And Water Mist Powerpoint Presentation Id 4414

Occupancy Hazard Classifications Interior Designers

Bol Com Dow S Fire And Explosion Index Hazard Classification Guide American

Hazard Classification 6 28 10 Fire Sprinkler System Flammability

Background Of Classification Problems The Explosion Hazard Classification Of Gases And Dusts Relative To Use Of Electrical Equipment The National Academies Press

Forest Fire Hazard Classification Download Table

Chemical Laboratory Unit Fire Sprinkler System Flammability
Q Tbn And9gcrrvunawdwzq84r3ahqpidx7qsts34ye9yqtipdv22uckvm7w6w Usqp Cau

Nfpa Journal In Compliance Nfpa 13 July August 14
09 Sfpe San Diego A Fundamental Approach Towards Fire Hazard Cl

Nfpa Hazard Classification System

Ghs Hazard Class And Hazard Category

Basic Guide To Nfpa 13 Occupancy And Commodity Classifications

Future Hazard Analysis In En Occupancy And Storage Classification Ppt Download

Hazardous Materials Classification Reference Teaching Supplies Classroom Fisher Scientific

Fire Extinguishers Fire Extinguisher Pro

Ghs Hazard Class And Hazard Category
Plos One Determining Fuel Moisture Thresholds To Assess Wildfire Hazard A Contribution To An Operational Early Warning System

Bilingual Hazard Material Write On Class Sign Aris Industrial Supply

Construction Concerns Classification Of Flammable And Combustible Liquids Fire Engineering

Hazardous Materials Classification Nfpa 704 Basics

Nfpa Hazard Classifications Defined Compliance First Inc

Classification Of Fire And Hazard Types As Per Nfpa Enggcyclopedia

Hazardous Materials Classification Hazard Sign Nfpa Guides Aluminum Metal Sign Ebay

Classification Of Fire And Hazard Types As Per Nfpa Enggcyclopedia
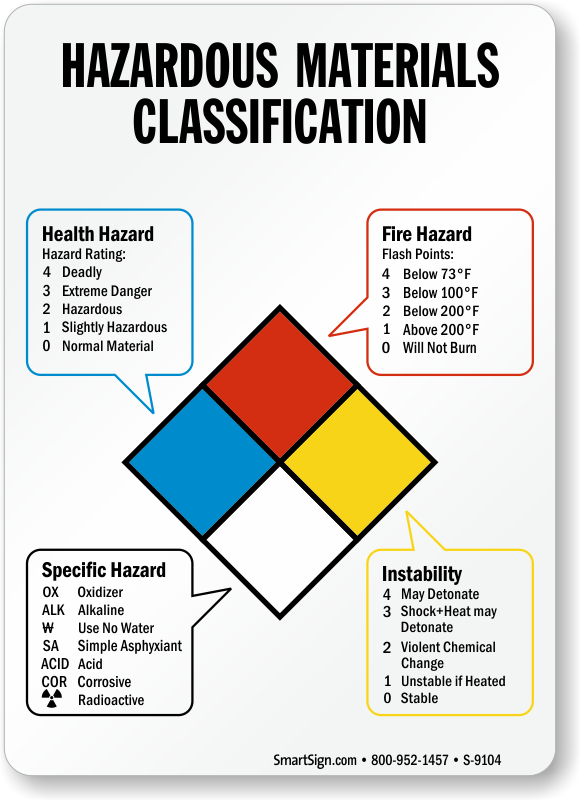
Hazardous Materials Classification Nfpa Guide Sign

Nmc Hmc14p 7 Hazardous Materials Classification Sign Health And Safety Poster Hazardous Materials Chemical Safety
1

Forest Fire Hazard Classification Download Table

Laser Classification Table Laser Safety Facts

Cers Chemical Hazard Classification Gasoline Nes

Fire Hazard Management Cholarisk

Gap 2 5 2 A Acetic Acid Explosion

Buckeye Fire Material Safety Data Sheet Carbon Dioxide Fire Extinguishant Industrial And Personal Safety Products From Onlinesafetydepot Com




