Nucleus Solitarius
The nucleus of the solitary tract, also known as the nucleus tractus solitarius (pl solitarii) is a pair of cell bodies found in the brainstemThis structure, along with its tract (the solitary tract or tractus solitarius), has far reaching impacts on many homeostatic systems within the body.
Nucleus solitarius. Microinjections of serotonin (5HT) delivered into the nucleus tractus solitarius (NTS) elicit opposite cardiovascular effects depending on the doses used;. Blood pressure and heart rate are decreased by low doses but increased by high doses To examine this apparent contradiction, we compared cardiovascular and sympathetic nerve responses elicited in anesthetized rats by using glass. Microinjections of serotonin (5HT) delivered into the nucleus tractus solitarius (NTS) elicit opposite cardiovascular effects depending on the doses used;.
The nucleus solitarius receives fibres carrying general visceral sensations through the vagus and glossopharyngeal nerves Through those afferents, and through connections with the reticular formation, the nucleus of solitary tract plays an important role in reflex control of respiratory and cardiovascular functions. The term solitary nucleus refers to a group of cells in the medulla that is involved in the sensory component of autonomic systems that control visceral organs, such as the heart and lungs It contains numerous subnuclei, which vary by species and method of identification Classically the nucleus is divided into five subnuclei defined on the basis of topology as observed with Nissl staining. Ghrelin administration to naïve female mice caused a higher increase in food intake, growth hormone secretion, Agrp mRNA expression in the arcuate nucleus and c‐Fos expression in the nucleus tractus solitarius (NTS) than in male mice In contrast, psychological stress caused a more sustained reduction in food intake in females than males.
In the human brainstem, the solitary nucleus (SN) (nucleus of the solitary tract, nucleus solitarius, nucleus tractus solitarii) is a series of purely sensory nuclei (clusters of nerve cell bodies) forming a vertical column of grey matter embedded in the medulla oblongataThrough the center of the SN runs the solitary tract, a white bundle of nerve fibers, including fibers from the facial. The first and most important terminal of this activity is the brainstem vagal nucleus tractus solitarius Its function, on which the vagal efferent inputs that control the splanchnic organs depend, is conditioned by the level of synaptic transmission within it In conclusion, on the basis of such a view, a selective pharmacological modulation. The nucleus tractus solitarius (NTS) of the medulla receives sensory input from different systemic and central receptors (eg, baroreceptors and chemoreceptors)Neural connections from the NTS modulate the activity of sympathetic neurons located in the rostral ventrolateral medulla, and the activity of parasympathetic neurons located in the dorsal vagal nucleus and nucleus ambiguus from which.
Http//wwwhandwrittentutorialscom This video is an overview of the Solitary Nucleus which is involved in gustation and visceral sensation For more entir. Nucleus see cellcell, in biology, the unit of structure and function of which all plants and animals are composed The cell is the smallest unit in the living organism that is capable of integrating the essential life processes There are many unicellular organisms, eg Click the link for more information , in biologynucleus, in physics, the. Blood pressure and heart rate are decreased by low doses but increased by high doses To examine this apparent contradiction, we compared cardiovascular and sympathetic nerve responses elicited in anesthetized rats by using glass.
Nucleus solitarius participates in the reflexes of the nerves innervating the nucleus, so it mediates cough reflex, carotid sinus reflex, gag reflex, and vomiting reflex The cough reflex is an involuntary protective reaction to nociceptive stimuli that serves to clear the throat from harmful objects. The nucleus of tractus solitarius is a brainstem nucleus on each side of the upper medulla It lies lateral to the dorsal nucleus of the vagus, to which it has many connecting neurones, and medial to the spinal tract and the nucleus of the trigeminal nerve. The term solitary nucleus refers to a group of cells in the medulla that is involved in the sensory component of autonomic systems that control visceral organs, such as the heart and lungs It contains numerous subnuclei, which vary by species and method of identification Classically the nucleus is divided into five subnuclei defined on the basis of topology as observed with Nissl staining.
The Nucleus tractus solitarius (NTS) in the caudal medulla is a gateway for a variety of cardiopulmonary afferents important for homeostatic regulation and defense against airway and cardiovascular insults and is a key central target potentially mediating the response habituation to these inputs. The gustatory portion of the nucleus solitarius receives special visceral afferent taste fibers from the facial and glossopharyngeal nerves Unlike the olfactory system, the gustatory system projects to the thalamus for relay to the cerebral cortex Brodmann area 43, the most ventral (opercular) part of the postcentral gyrus, is the cortical. Cells in the inferior ganglion IX).
The aim of this study was to characterize adenosine receptors located in the nucleus tractus solitarius (NTS) that mediate decreases in blood pressure in the anaesthetized rat To determine the adenosine receptor subtype involved, a range of selective agonists and antagonists were studied and their relative potencies evaluated 2. The Nucleus tractus solitarius (NTS) in the caudal medulla is a gateway for a variety of cardiopulmonary afferents important for homeostatic regulation and defense against airway and cardiovascular insults and is a key central target potentially mediating the response habituation to these inputs. To determine the role of the nucleus tractus solitarius (NTS) in the tonic maintenance of arterial pressure (AP) following chronic baroreceptor denervation, the present study examined the effect of inhibition of the NTS on AP in chronic sinoaortic denervated (SAD) and control rats.
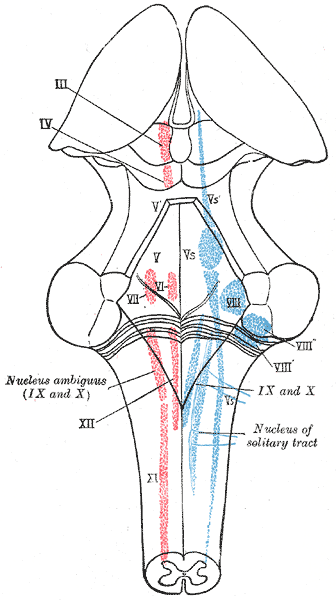
Other articles where Nucleus ambiguus is discussed human nervous system Parasympathetic nervous system the ventral medulla called the nucleus ambiguus, while those that control functions of the gastrointestinal tract arise from the dorsal vagal nucleus After exiting the medulla in the vagus nerve and traveling to their respective organs, the fibres synapse on ganglion cells embedded in. The nucleus solitarius receives fibres carrying general visceral sensations through the vagus and glossopharyngeal nerves Through those afferents, and through connections with the reticular formation, the nucleus of solitary tract plays an important role in reflex control of respiratory and cardiovascular functions. Abstract The rostral nucleus of the solitary tract (rNST) is the first central relay in the gustatory pathway While previous investigations have provided a wealth of information on the pattern of central terminations of gustatory afferent fibers, the morphology of synaptic connections of rNST neurons and responses of second order neurons to taste stimuli applied to the tongue, little is.
In the human brainstem, the solitary nucleus (SN) (nucleus of the solitary tract, nucleus solitarius, nucleus tractus solitarii) is a series of purely sensory nuclei (clusters of nerve cell bodies) forming a vertical column of grey matter embedded in the medulla oblongataThrough the center of the SN runs the solitary tract, a white bundle of nerve fibers, including fibers from the facial. Gray matter located in the dorsomedial part of the medulla oblongata associated with the solitary tract The solitary nucleus receives inputs from most organ systems including the terminations of the facial, glossopharyngeal, and vagus nerves It is a major coordinator of autonomic nervous system regulation of cardiovascular, respiratory, gustatory, gastrointestinal, and chemoreceptive aspects. Nucleus Solitarius's foodie profile on Zomato Check out Nucleus Solitarius's restaurant reviews, favorite restaurants, wishlist and other activity in Toronto and more on Zomato Follow Nucleus Solitarius on Zomato.
Define nucleus of the tractus solitarius nucleus of the tractus solitarius synonyms, nucleus of the tractus solitarius pronunciation, nucleus of the tractus solitarius translation, English dictionary definition of nucleus of the tractus solitarius n pl nu·cle·i or nu·cle·us·es 1 A central or essential part around which other parts are. Gray matter located in the dorsomedial part of the medulla oblongata associated with the solitary tract The solitary nucleus receives inputs from most organ systems including the terminations of the facial, glossopharyngeal, and vagus nerves It is a major coordinator of autonomic nervous system regulation of cardiovascular, respiratory, gustatory, gastrointestinal, and chemoreceptive aspects. The red nucleus is one of the brainstem nuclei and part of the extrapyramidal systemThe red nuclei are situated within the tegmentum of the midbrain (the part between the cerebral peduncles and the quadrigeminal plate)It consists of a larger neorubrum and smaller paleorubrum Function It receives afferent fibers from several locations within the diencephalon.
In addition, UvnäsMoberg et al suggested that projection of hypothalamic OT enhances the activity of alpha 2adrenoreceptors of the NTS (nucleus tractus solitarius) and LC (locus coeruleus), which then can influence the noradrenergic neurons projecting to the CRF neurons in the hypothalamus (UvnäsMoberg et al, 15). Lesions • Paralysis causes lateral rectus palsy, leading to medial deviation of the affected eye and diplopia o CN VII Main Motor Nucleus • To all the muscles of facial expression • NOTE the upper face receives bilateral innervation BUT the lower face receives contralateral innervation • REFER TO Bell’s PALSY Superior Salivatory nucleus • Located posterolateral to the motor nucleus. The nucleus of tractus solitarius, also known as the nucleus of the solitary tract or simply the solitary nucleus, is a purely sensory nucleus located in the dorsolateral medulla oblongata and lower ponsIt receives many sensory inputs including taste information and sensory information from the middle ear, contributing to the facial, glossopharyngeal and vagus nerves.
The Nucleus Tractus Solitarius Neuroanatomic, Neurochemical and Functional Aspects Arch Int Physiol Biochim Biophys 1991 Sep;99(5)A352 doi / Article in French Author A Jean 1 Affiliation 1 Laboratoire de Neurobiologie fonctionnelle. Nucleus and Tractus Solitarius Function Nucleus receives input from the viscera and taste buds (viscerosensory) Pathway Caudal portion of nucleus solitarius receives input from viscera (cell bodies in the inferior ganglion X) and from the carotid sinus (baroreceptors;. However, how the drug affects the central nervous system to promote satiety is not fully elucidated Fortin et al identified a subset of GABAergic neurons in the nucleus tractus solitarius (NTS) that.
The nucleus of the tractus solitarius (NTS) is a brain stem region critical to many physiologic processes and has been implicated in addiction to multiple classes of abused drugs, including alcohol (EtOH) That said, the mechanism by which EtOH modulates NTS neurocircuit activity is not well characterized and has yet to be examined utilizing. The gustatory portion of the nucleus solitarius receives special visceral afferent taste fibers from the facial and glossopharyngeal nerves Unlike the olfactory system, the gustatory system projects to the thalamus for relay to the cerebral cortex Brodmann area 43, the most ventral (opercular) part of the postcentral gyrus, is the cortical. Lesions • Paralysis causes lateral rectus palsy, leading to medial deviation of the affected eye and diplopia o CN VII Main Motor Nucleus • To all the muscles of facial expression • NOTE the upper face receives bilateral innervation BUT the lower face receives contralateral innervation • REFER TO Bell’s PALSY Superior Salivatory nucleus • Located posterolateral to the motor nucleus.
Nucleus solitarius is the nucleus in the medulla that receives afferent information from the larynx (via cranial nerve X) and posterior pharynx and mediates the gag and cough reflexes (cranial nerves IX and X). This page includes the following topics and synonyms Brain Stem Anatomy, Brain Stem, Brainstem, Cranial Nerve Nucleus, Nucleus Solitarius, Nucleus Ambiguous, Somatic Motor Nucleii, Visceral Motor Nucleii, Visceral Sensory Nucleii, Somatic Sensory Nucleii. The nucleus ambiguus receives short connecting fibers from the neighboring cranial sensory nuclei, ie, the spinal trigeminal nucleus and nucleus solitarius These fibers complete reflex arcs controlling swallowing, coughing, vomiting and control laryngeal motor output The cortical input to the nucleus ambiguus is bilateral and indirect.
The nucleus tractus solitarius (NTS) region in the rat has been shown to receive arginine vasopressin (AVP) and oxytocin (OT) neurophysincontaining neuronal projections from the suprachiasmatic (SNC) and paraventricular nucleus (PVN) Thus, vasopressin and oxytocin might have central influences on. Immunocytochemical studies on the nucleus of the tractus solitarius and adjacent areas of the dorsal medulla of the rat demonstrate the existence of somatostatin immunoreactive nerve cell bodies. VAH involves plasticity in arterial chemoreceptors and the CNS eg nucleus tractus solitarius (NTS), although the signals for this plasticity are not known We hypothesized that hypoxia inducible factor 1α (HIF‐1α), an O 2 ‐sensitive transcription factor, is necessary in the NTS for normal VAH.
The nucleus tractus solitarius a portal for visceral afferent signal processing, energy status assessment and integration of their combined effects on food intake Int J Obes (Lond) 09;33(Suppl_1)S11–S15 View this article via PubMed Google Scholar Berthoud HR Interactions between the “cognitive” and “metabolic” brain in the. In addition, UvnäsMoberg et al suggested that projection of hypothalamic OT enhances the activity of alpha 2adrenoreceptors of the NTS (nucleus tractus solitarius) and LC (locus coeruleus), which then can influence the noradrenergic neurons projecting to the CRF neurons in the hypothalamus (UvnäsMoberg et al, 15). This page includes the following topics and synonyms Brain Stem Anatomy, Brain Stem, Brainstem, Cranial Nerve Nucleus, Nucleus Solitarius, Nucleus Ambiguous, Somatic Motor Nucleii, Visceral Motor Nucleii, Visceral Sensory Nucleii, Somatic Sensory Nucleii.
Cite this entry as Mendoza JE (11) Nucleus Solitarius In Kreutzer JS, DeLuca J, Caplan B (eds) Encyclopedia of Clinical Neuropsychology. Nucleus Solitarius (n) 1 Gray matter located in the dorsomedial part of the MEDULLA OBLONGATA associated with the solitary tract The solitary nucleus receives inputs from most organ systems including the terminations of the facial, glossopharyngeal, and vagus nerves It is a major coordinator of AUTONOMIC NERVOUS SYSTEM regulation of. As well as being interrelated to vegetative activity and motor coordination of talking and deglution, it has also been attributed with regulating bloodpressure, controlling visceral pain, thermal regulation and motivationalaffective responses to pain due to its connections with the solitary nucleus, raphe magnus, parabrachial area and amygdaloid nucleus (trigeminalparabrachialamygdaloid.
Immunocytochemical studies on the nucleus of the tractus solitarius and adjacent areas of the dorsal medulla of the rat demonstrate the existence of somatostatin immunoreactive nerve cell bodies. Nucleus solitarius is the recipient of all visceral afferents, and an essential part of the regulatory centers of the internal homeostasis, through its multiple projections with cardiorespiratory and gastrointestinal regulatory centers. This research was undertaken to determine whether injection of SP into the nucleus tractus solitarius (NTS) of developing beagles alters laryngeal adductor motor activity Six animals, 57 to 78 days of age, underwent stereotactic injection of 5 to 10 μL of SP into the region of the NTS, identified by electrical stimulation of the ipsilateral.
In the human brain, the solitary nucleus (nucleus of the solitary tract, nucleus solitarius, nucleus tractus solitarii, NTS) is a series of nuclei (clusters of nerve cell bodies) forming a vertical column of grey matter embedded in the medulla oblongataThrough the center of the NTS runs the solitary tract, a white bundle of nerve fibers, including fibers from the facial, glossopharyngeal and. In the human brainstem, the solitary nucleus (SN) (nucleus of the solitary tract, nucleus solitarius, nucleus tractus solitarii) is a series of purely sensory nuclei (clusters of nerve cell bodies) forming a vertical column of grey matter embedded in the medulla oblongataThrough the center of the SN runs the solitary tract, a white bundle of nerve fibers, including fibers from the facial. Nucleus and Tractus Solitarius Function Nucleus receives input from the viscera and taste buds (viscerosensory) Pathway Caudal portion of nucleus solitarius receives input from viscera (cell bodies in the inferior ganglion X) and from the carotid sinus (baroreceptors;.
The nucleus tractus solitarius (NTS) is the principal visceral sensory nucleus in the brain and comprises neurochemically and biophysically distinct neurons located in the dorsomedial medulla oblongata. Define nucleus of the tractus solitarius nucleus of the tractus solitarius synonyms, nucleus of the tractus solitarius pronunciation, nucleus of the tractus solitarius translation, English dictionary definition of nucleus of the tractus solitarius n pl nu·cle·i or nu·cle·us·es 1 A central or essential part around which other parts are. What is the nucleus solitarius?.
In addition, UvnäsMoberg et al suggested that projection of hypothalamic OT enhances the activity of alpha 2adrenoreceptors of the NTS (nucleus tractus solitarius) and LC (locus coeruleus), which then can influence the noradrenergic neurons projecting to the CRF neurons in the hypothalamus (UvnäsMoberg et al, 15). Liraglutide is an approved medication that is prescribed in part for its ability to lower food intake and body weight Liraglutide is a known glucagonlike peptide1 receptor (GLP1R) agonist;. Nucleus Solitarius (n) 1 Gray matter located in the dorsomedial part of the MEDULLA OBLONGATA associated with the solitary tract The solitary nucleus receives inputs from most organ systems including the terminations of the facial, glossopharyngeal, and vagus nerves It is a major coordinator of AUTONOMIC NERVOUS SYSTEM regulation of.
The nucleus tractus solitarius a portal for visceral afferent signal processing, energy status assessment and integration of their combined effects on food intake Int J Obes (Lond) 09;33(Suppl_1)S11–S15 View this article via PubMed Google Scholar Berthoud HR Interactions between the “cognitive” and “metabolic” brain in the. Recent work has shown that most cells in the rostral, gustatory portion of the nucleus tractus solitarius (rNTS) in awake, freely licking rats show lickrelated firing However, the relationship between tasterelated and lickrelated activity in rNTS. Nucleus solitarius is the recipient of all visceral afferents, and an essential part of the regulatory centers of the internal homeostasis, through its multiple projections with cardiorespiratory and gastrointestinal regulatory centers.
Cells in the inferior ganglion IX). The solitary tract (Latin tractus solitarius, or fasciculus solitarius) is a compact fiber bundle that extends longitudinally through the posterolateral region of the medullaThe solitary tract is surrounded by the nucleus of the solitary tract, and descends to the upper cervical segments of the spinal cordIt was first named by Theodor Meynert in 1872. Nucleus solitarius participates in the reflexes of the nerves innervating the nucleus, so it mediates cough reflex, carotid sinus reflex, gag reflex, and vomiting reflex The cough reflex is an involuntary protective reaction to nociceptive stimuli that serves to clear the throat from harmful objects.

Targets Of Axons From Cells In The Nucleus Tractus Solitarius Download Scientific Diagram

Off Topic Your Gonads Are Innervated By Your Cranial Nerves Sauropod Vertebra Picture Of The Week
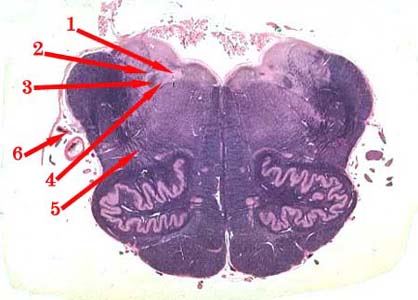
Slide19b
Nucleus Solitarius のギャラリー

The Cranial Nerves And Cranial Nerve Nuclei Of The Brain Stem Objectives Learn The Name And Numerical Designation Of Each Of The Twelve Cranial Nerves Learn The Names And Functions Of The

Facial Nerve Cnvii Mednotes
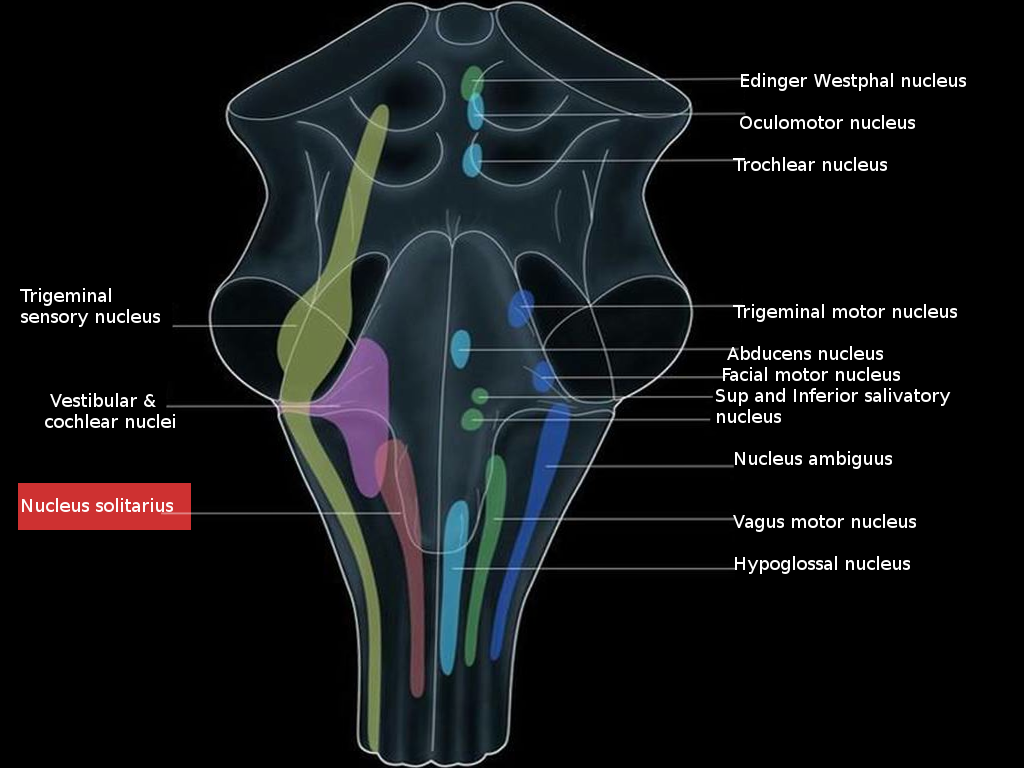
Neuroanatomy Nucleus Solitarius Article
Http Www Neuroanatomy Wisc Edu Coursebook Webstem11 13 Pdf

Brain Stem
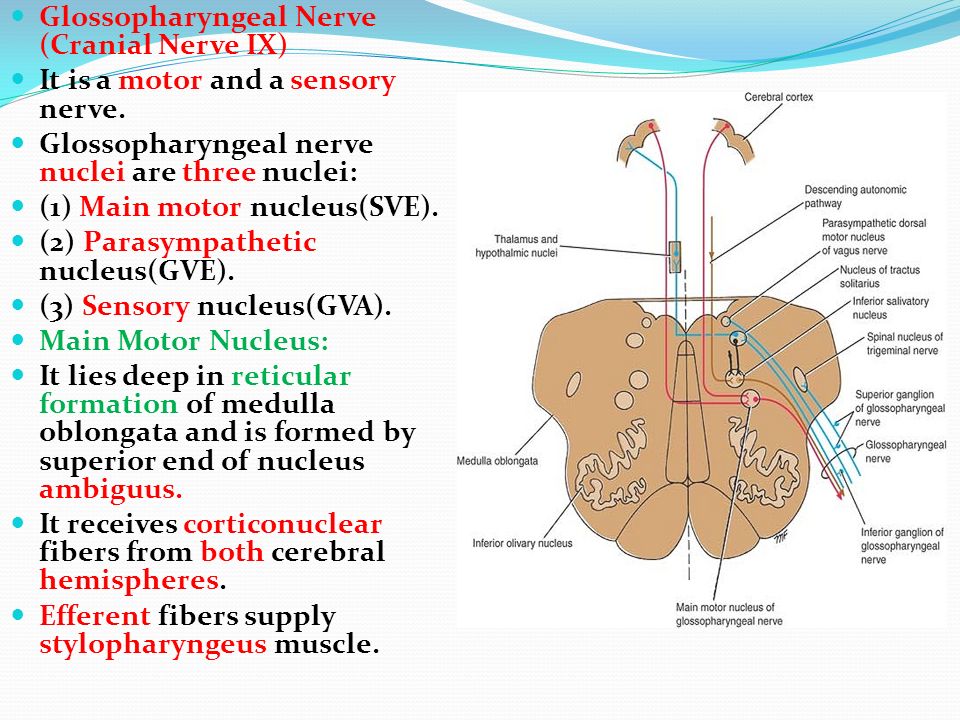
Cranial Neves Ix X Xi Dr Nimir Dr Safaa Cranial Neves Ix X Xi Dr Nimir Dr Safaa Ppt Video Online Download

Cranial Nerve X Vagus Nerve Cross Sectional Nuclei Grepmed
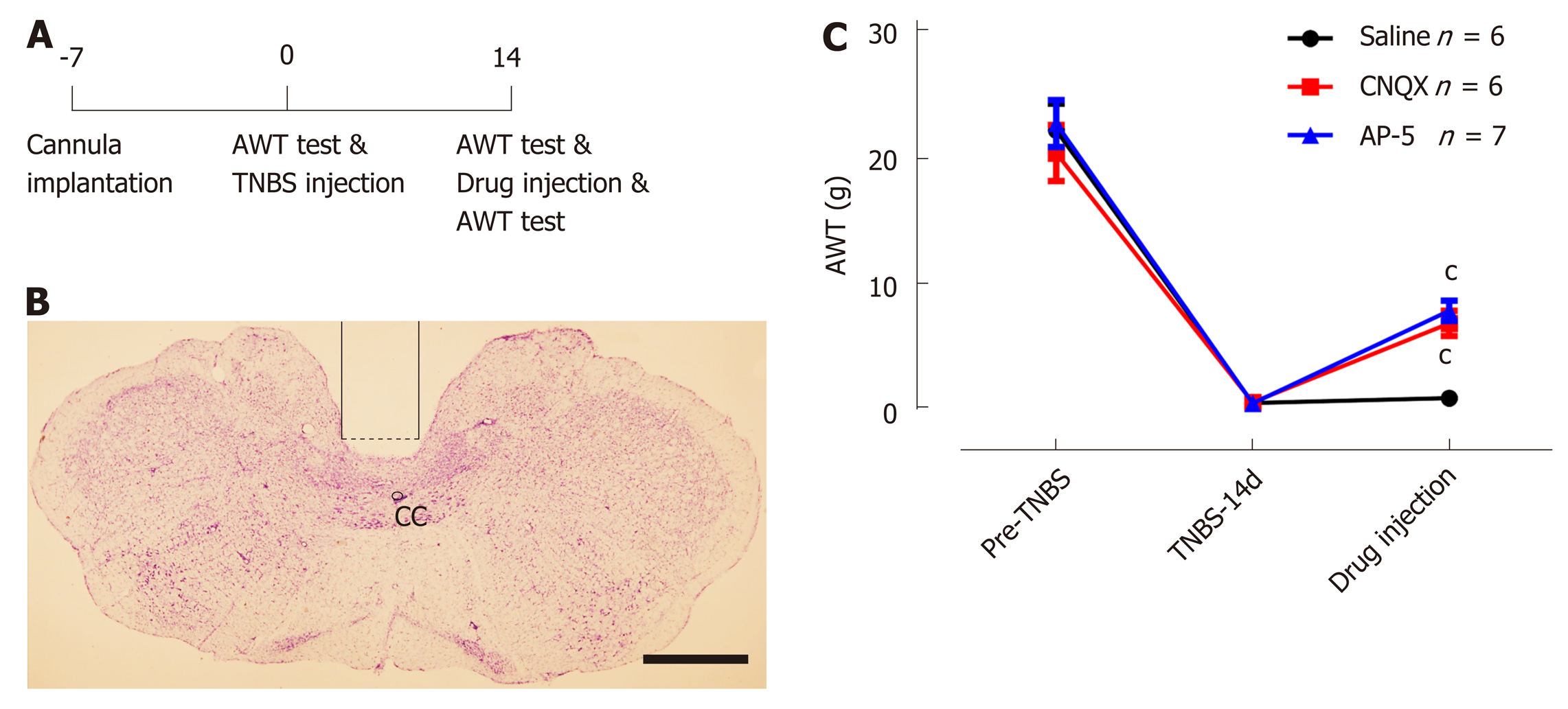
Nucleus Tractus Solitarius Mediates Hyperalgesia Induced By Chronic Pancreatitis In Rats

What Are Cranial Nerve Nuclei Biology Stack Exchange


Solitary Nucleus Wikiwand
Nucleus Tractus Solitarius Mediates Hyperalgesia Induced By Chronic Pancreatitis In Rats
Nucleus Of The Solitary Tract Psychology Wiki Fandom

Jci Insight Leptin Receptor Expressing Nucleus Tractus Solitarius Neurons Suppress Food Intake Independently Of Glp1 In Mice
N Neurology Org Content Neurology 12 1187 Full Text Pdf
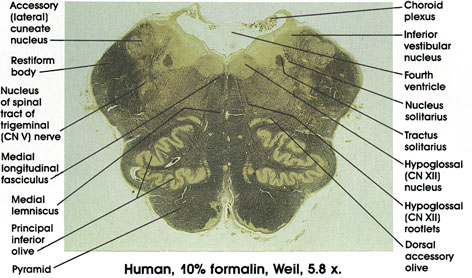
Anatomy Atlases Atlas Of Microscopic Anatomy Section 1 Cells

Functional Neuroplasticity In The Nucleus Tractus Solitarius And Increased Risk Of Sudden Death In Mice With Acquired Temporal Lobe Epilepsy Epilepsy Foundation
Neuroanatomy Online Lab 6 Auditory Vestibular Gustatory And Olfaction Systems The Central Gustatory System

Brain Stem

Autonomic Regulation Of Bp Key Cns Nuclei Nucleus Tractus Solitarius Download Scientific Diagram

Glossopharyngeal Nucleus Ambiguus Motor Stylopharyngeus Muscle Soft Palate Sensory Nucleus Tract Cranial Nerves Cranial Nerves Mnemonic Glossopharyngeal Nerve

Solitary Tract Wikipedia
Q Tbn And9gcssuisvhnirtxz1t9nn 231inrqir0s2hgm4qa8orf9ubohmbgr Usqp Cau
Plos One Responses Of Nucleus Tractus Solitarius Nts Early And Late Neurons To Blood Pressure Changes In Anesthetized F344 Rats

Nucleus Tractus Solitarius Medical Mnemonics Medical Anatomy Dentistry

Nucleus Ambiguus An Overview Sciencedirect Topics

Nucleus Of Tractus Solitarius Radiology Reference Article Radiopaedia Org

Nucleus Of Tractus Solitarius Radiology Reference Article Radiopaedia Org

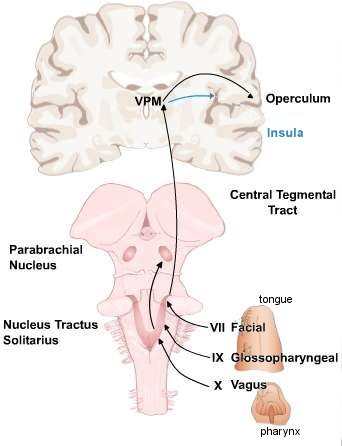
Gustatory Pathway Taste Sensations Are Transmitted By The Facial Nerves Cn Vii From The Anterior Two Thirds Of The Tongue And By The Glossopharyngeal Nerves

Central Afferents To The Nucleus Of The Solitary Tract In Rats And Mice Gasparini Journal Of Comparative Neurology Wiley Online Library

D12 L2 Aj Flashcards Quizlet
Q Tbn And9gcs X3eg0rk8k9obfjowiqsulkwpfpyzc4ge63igh62qzmyexrmt Usqp Cau

Schematic Diagram Of Vagal Nuclei A Depicted Here Is An Anterior Download Scientific Diagram

Differentiation Of Autonomic Reflex Control Begins With Cellular Mechanisms At The First Synapse Within The Nucleus Tractus Solitarius

Calcitonin Receptor Neurons In The Mouse Nucleus Tractus Solitarius Control Energy Balance Via The Non Aversive Suppression Of Feeding Sciencedirect
Academic Oup Com Chemse Article Pdf 21 3 367 21 3 367 Pdf

Ultrastructural Organization Of The Interstitial Subnucleus Of The Nucleus Of The Tractus Solitarius In The Cat Identification Of Vagal Afferents Springerlink

192 Cranial Nerves Ix X Xi Flashcards Quizlet
Nerve Related To Nucleus Tractus Solitarius Mnemonics

Cranial Nerves And Cranial Nerve Nuclei Neuroanatomy An Illustrated Colour Text 4 Ed
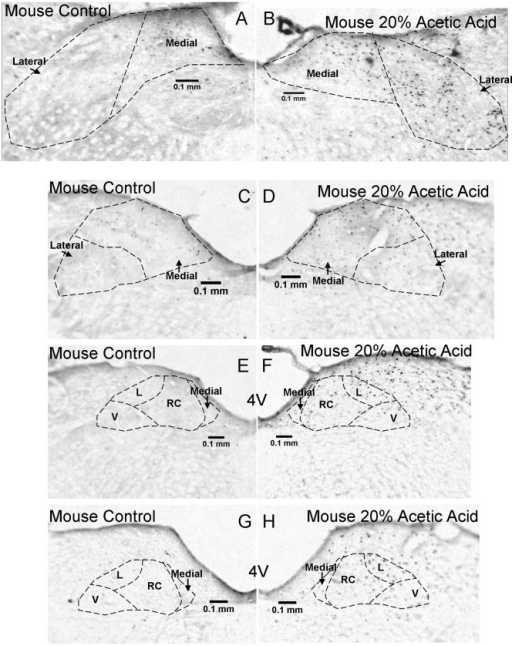
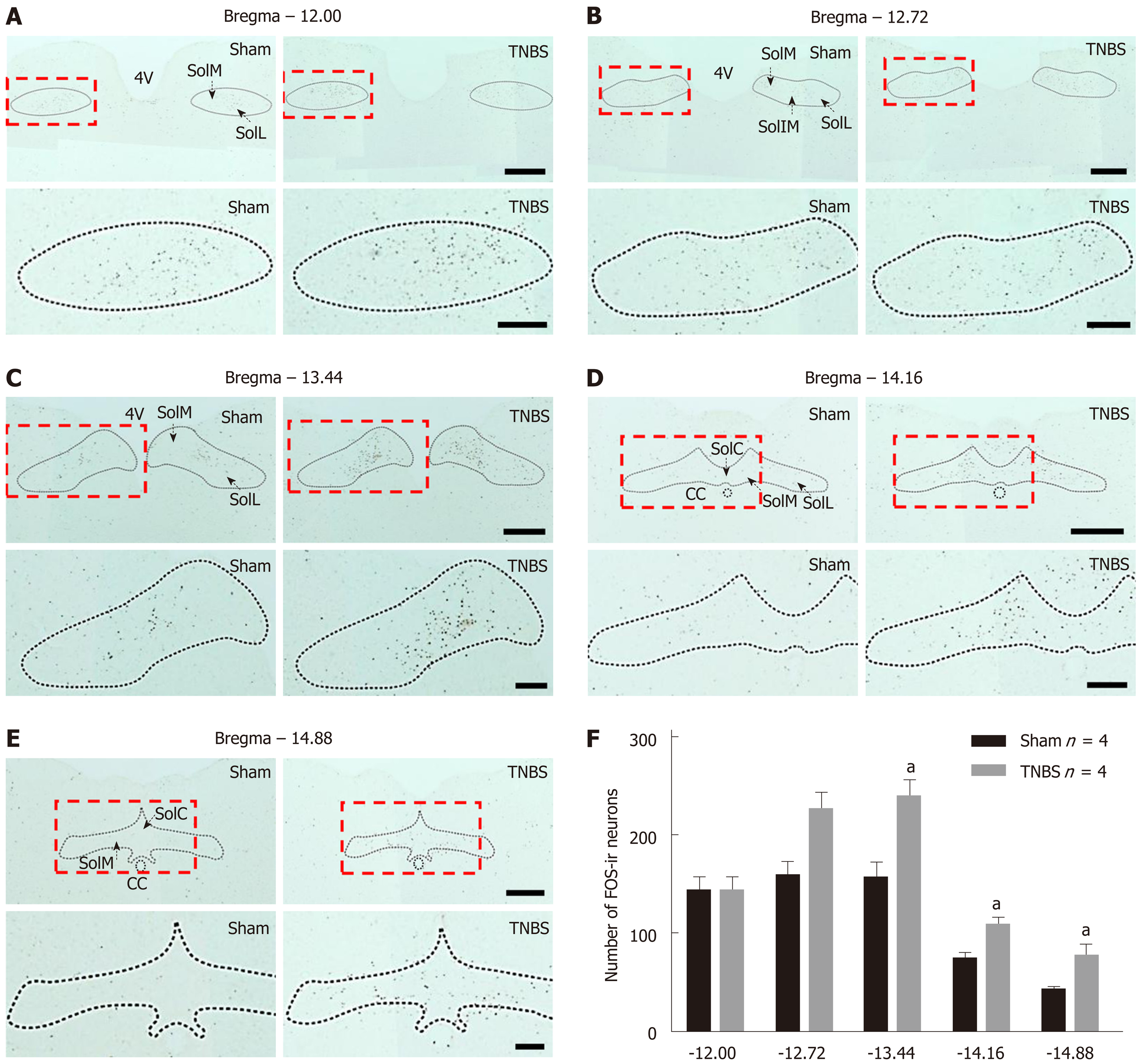
Additional C Fos Labeled Sections Through The Nucleus T Open I
Plos One Responses Of Nucleus Tractus Solitarius Nts Early And Late Neurons To Blood Pressure Changes In Anesthetized F344 Rats

Figure 2 Neural Circuits And Mediators Regulating Swallowing In The Brainstem Gi Motility Online

Key Role Of 5 Ht3 Receptors In The Nucleus Tractus Solitarii In Cardiovagal Stress Reactivity Sciencedirect
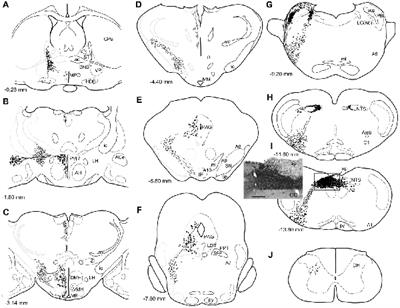
Frontiers Differential Ascending Projections From The Male Rat Caudal Nucleus Of The Tractus Solitarius An Interface Between Local Microcircuits And Global Macrocircuits Frontiers In Neuroanatomy

Nucleus Tractus Solitarius The Science Portal

Nucleus Tractus Solitarius

Brain Stem
Http Www Neuroanatomy Wisc Edu Coursebook Webstem11 13 Pdf

Brain Stem
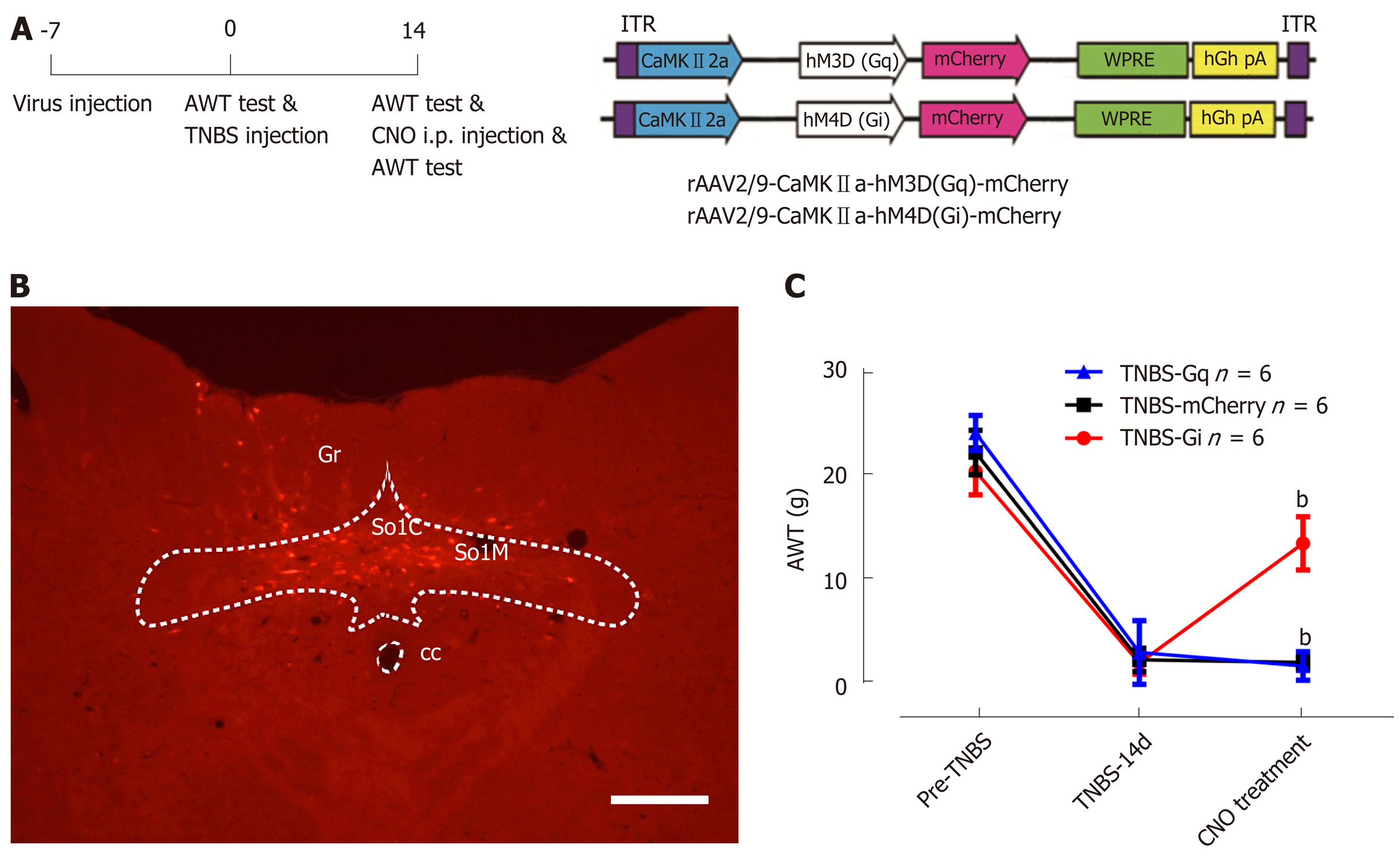
Nucleus Tractus Solitarius Mediates Hyperalgesia Induced By Chronic Pancreatitis In Rats

Cranial Nerve Overview Applied Anatomy
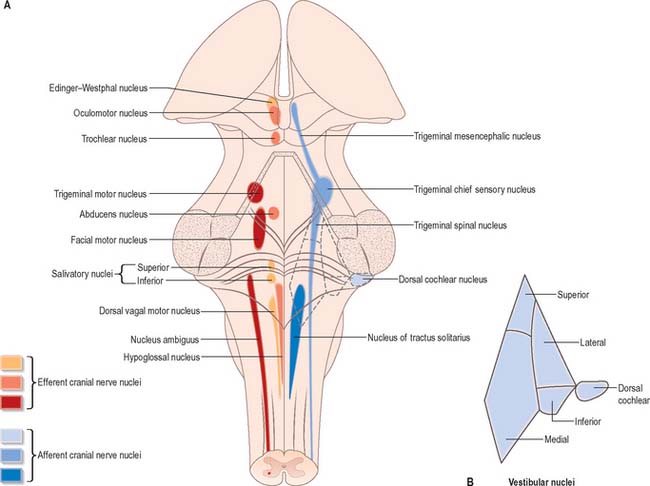
Brain Stem Clinical Gate
Nucleus Tractus Solitarius Springerlink
Major Vagal Nerve Branches And Central Projections From The Nucleus Download Scientific Diagram

Neuro Brainstem 2 Flashcards Quizlet
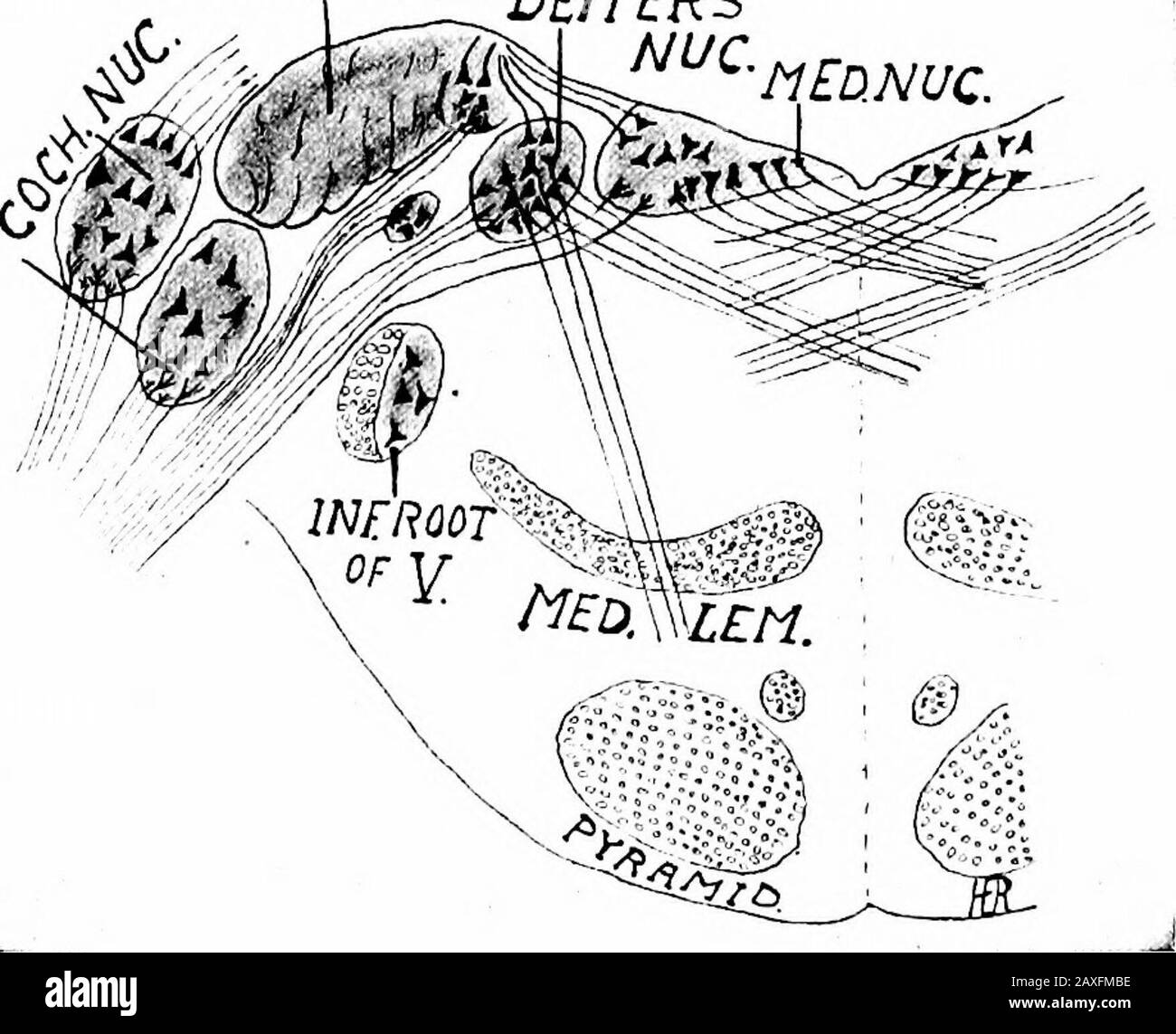
A Manual Of Anatomy Fig 306 A Diagram Of The Probable Pathways Of Gustatory Impulses Eestbody Deitersnuc Fig 307 Diagram Of The Nuclei Of Termination Of The Vestibular Nerve And Their Higher Connections
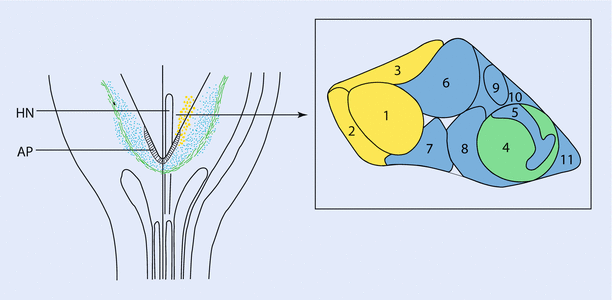
3 B Disfuncties Van Hersenen En Zintuigen Overzicht Van De Hersenzenuwen En Hun Functies Studeersnel
Slide17c

Figure 3 Physiology Of Oral Cavity Pharynx And Upper Esophageal Sphincter Gi Motility Online

Top Pdf Nucleus Tractus Of Solitarius 1library
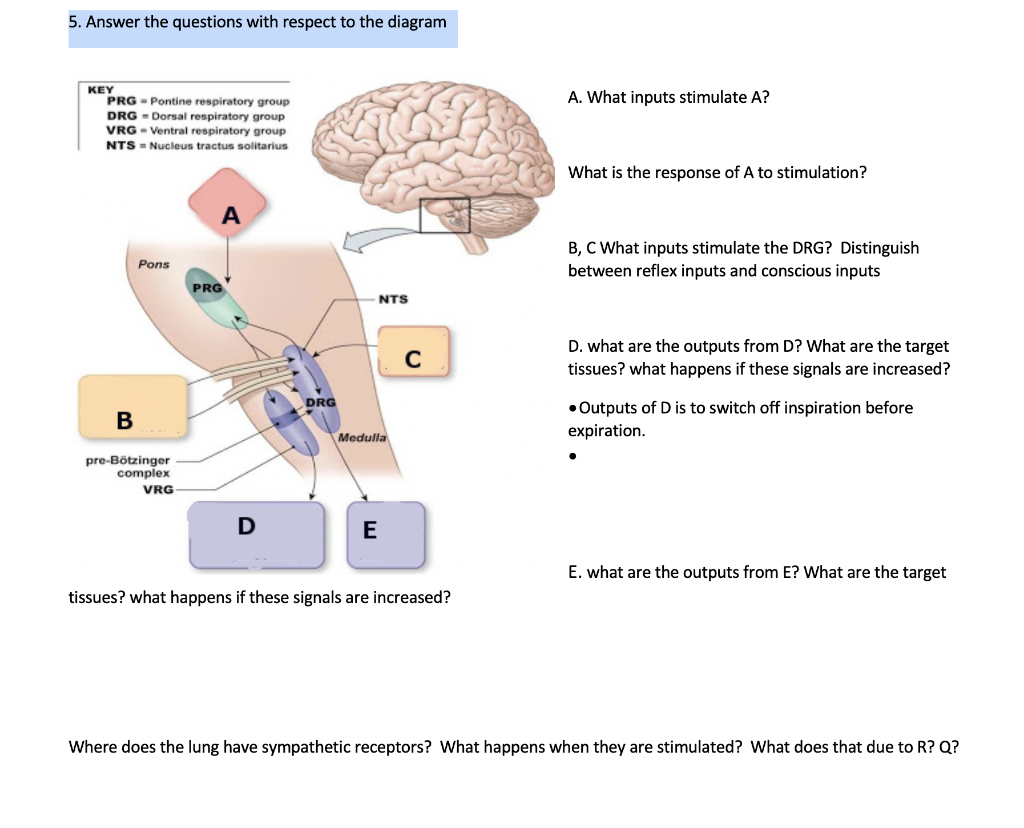
Solved 5 Answer The Questions With Respect To The Diagram Chegg Com
Nanopdf Com Download Cranial Nerves Amp Cranial Nerve Nuclei Pdf
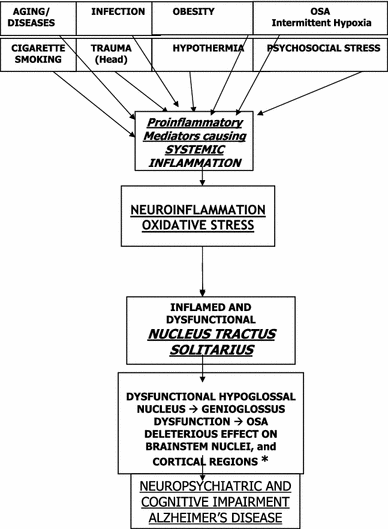
Dysfunctional Nucleus Tractus Solitarius Its Crucial Role In Promoting Neuropathogentic Cascade Of Alzheimer S Dementia A Novel Hypothesis Springerlink
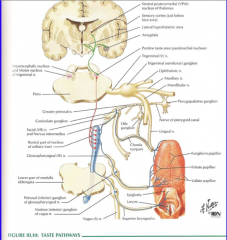
The Sensory Cranial Nerves Flashcards Cram Com
Nts Brainstem Wiki
Nts Brainstem Wiki
Rnts Definition Rostral Nucleus Tractus Solitarius Abbreviation Finder
:background_color(FFFFFF):format(jpeg)/images/article/en/the-solitary-tract-and-nucleus/eKWPib8aNwf7o36WMNrEdg_SLRXRbEIP0AhtEAoPt3wHg_Nucleus_n._hypoglossi_02.png)
Solitary Tract And Nucleus Anatomy And Function Kenhub
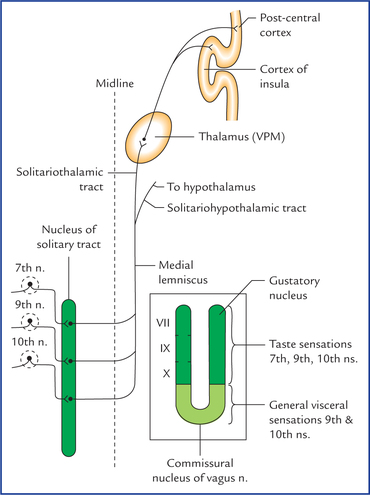
Nuclei Neupsy Key
Q Tbn And9gcss Rijtffltg6csl8qeozpmhduabbygbhlj1oivxabqgk4f Rp Usqp Cau
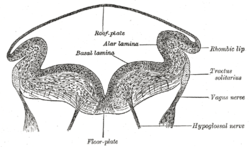
Solitary Nucleus Wikipedia
Neurology Uams Edu Wp Content Uploads Sites 49 18 03 Cn Marszalek Pdf

Nucleus Ambiguus An Overview Sciencedirect Topics
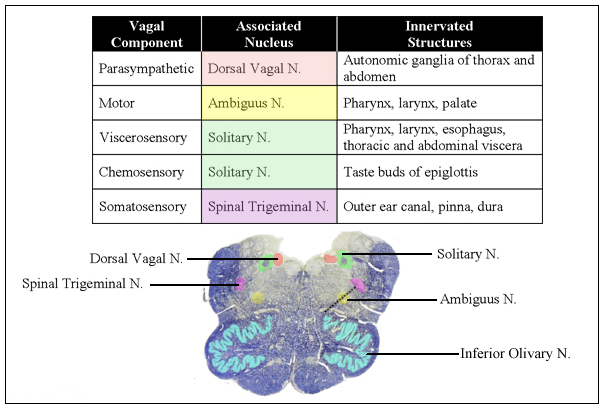
Neuroanatomy Online Lab 10 Cranial Nerve Nuclei And Brain Stem Circulation Cranial Nerve X Vagus Nerve

Glossopharyngeal Nerve Radiology Key

Representative Maps Of C Fos Expression In The Nucleus Tractus Download Scientific Diagram
Solitary Tract And Nucleus Anatomy And Function Kenhub

Aldosterone Target Neurons In The Nucleus Tractus Solitarius Drive Sodium Appetite Journal Of Neuroscience

Nucleus Of Tractus Solitarius Radiology Reference Article Radiopaedia Org
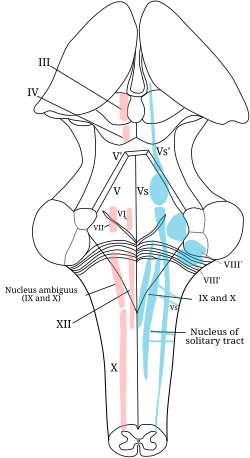
Solitary Nucleus Wikipedia

Anatomy Of The Brain Stem Ppt Download

Nucleus Solitarius Semantic Scholar

On A Hitherto Undescribed Nucleus Lateral To The Fasciculus Solitarius Mellus 1903 American Journal Of Anatomy Wiley Online Library

Cranial Nerve Nuclei Mednotes

Nucleus Solitarius Drone Fest

The Regulation Of Appetite Notes Nucleus Tractus Solitarii Nts Introduction
:watermark(/images/watermark_5000_10percent.png,0,0,0):watermark(/images/logo_url.png,-10,-10,0):format(jpeg)/images/atlas_overview_image/50/eQBBsjAWg0hPPdNKLDnIA_brainstem-and-related-structures_english.jpg)
Cranial Nerve Nuclei Anatomy And Embryology Kenhub
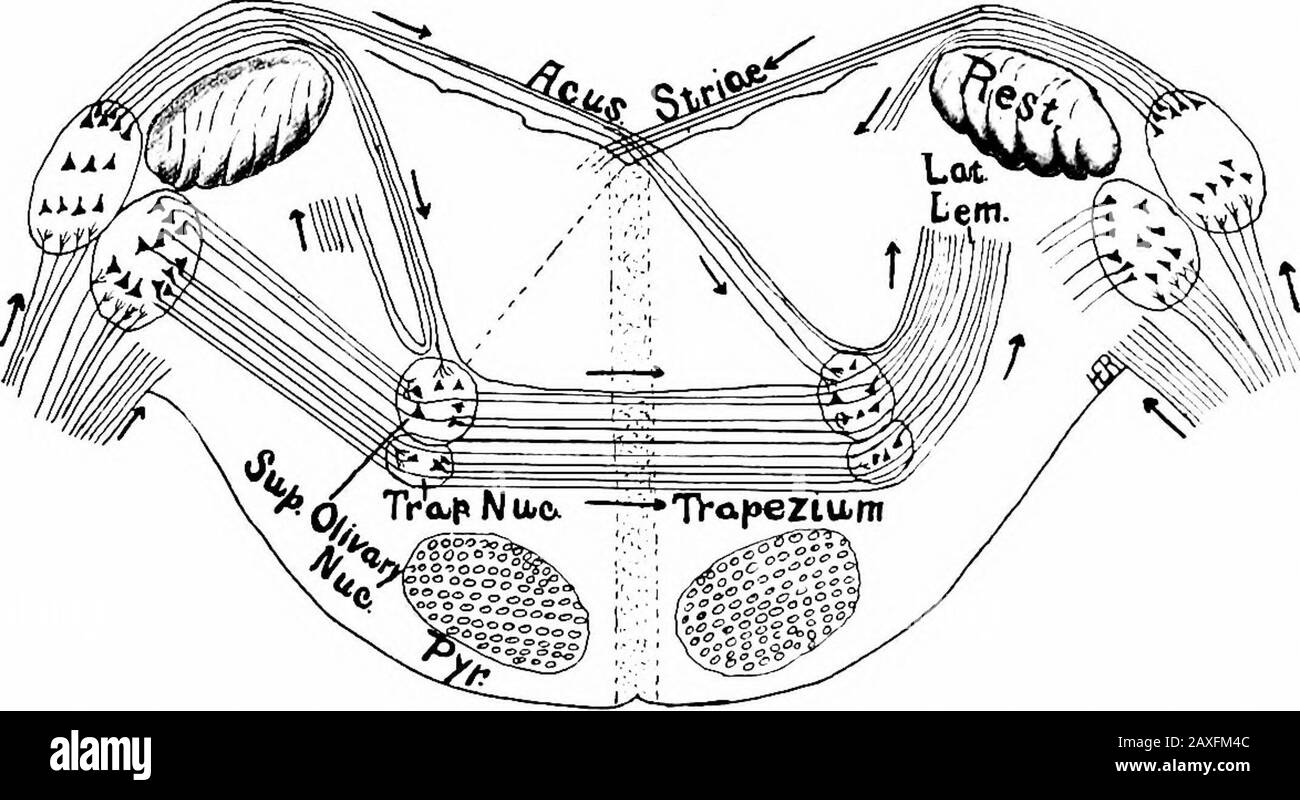
A Manual Of Anatomy Fig 307 Diagram Of The Nuclei Of Termination Of The Vestibular Nerve And Their Higher Connections The Auditory Pathway 423 Glossopharyngeal And Vagal Nerves The First Neuron Of
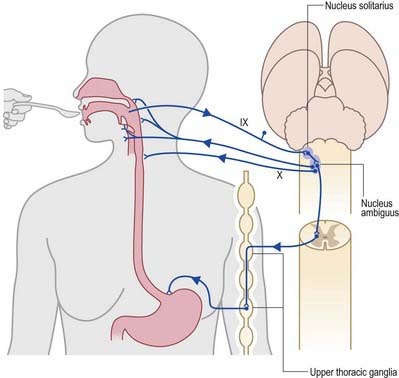
Brain Stem Neupsy Key
2

Nucleus Of The Solitary Tract Medullary Reflexes And Clinical Implications Semantic Scholar

Xmlinkhub
Q Tbn And9gcqjyr6u4kgnt0xtz010laxmxzsqdg6v5 Ypfndtajdykn4b Dxz Usqp Cau

Figure 1 From The Effects Of Chronic Hypoxia And Substance P On The Chemosensitive Response Of Individual Nucleus Tractus Solitarius Nts Neurons From Adult Rats Semantic Scholar

Solitary Tract Wikipedia

The Effect Of Nucleus Tractus Solitarius Nitric Oxidergic Neurons On
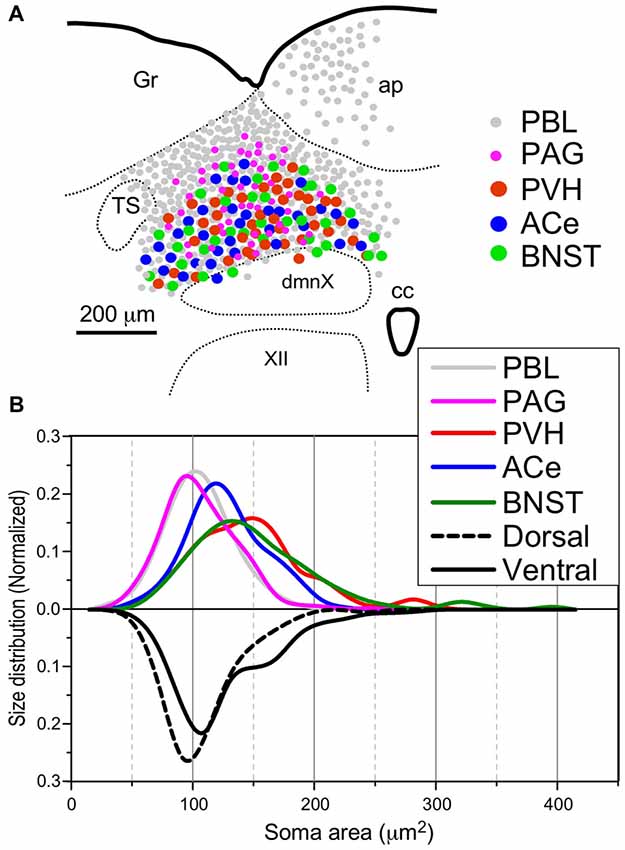
Frontiers Differential Ascending Projections From The Male Rat Caudal Nucleus Of The Tractus Solitarius An Interface Between Local Microcircuits And Global Macrocircuits Frontiers In Neuroanatomy
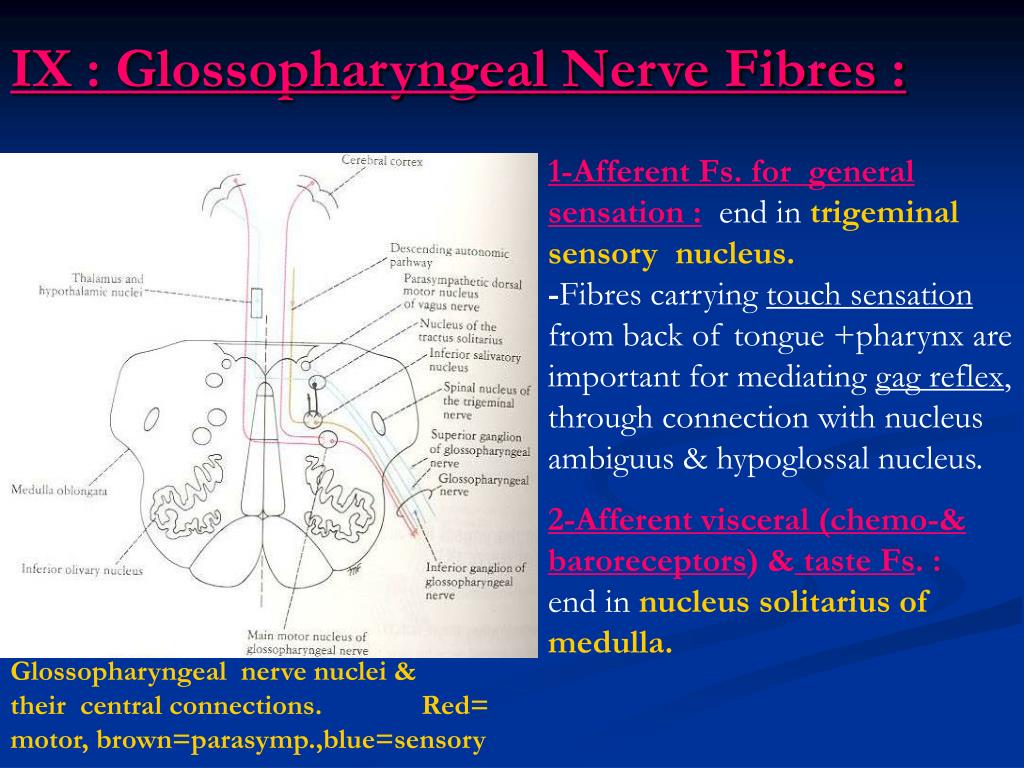
Ppt Cranial Nerves Cranial Nerve Nuclei Powerpoint Presentation Id

No Evidence Of A Role For Neuronal Nitric Oxide Synthase In The Nucleus Tractus Solitarius In Ventilatory Responses To Acute Or Chronic Hypoxia In Awake Rats Journal Of Applied Physiology

Nucleus Of The Solitary Tract Medullary Reflexes And Clinical Implications Neurology




